
Energy storage devices called superapacitors can be recharged many more times than batteries, but the total amount of energy they can store is limited. This means that the devices are useful for providing intense bursts of power to supplement batteries but less so for applications that require steady power over a long period, such as running a laptop or an engine.
Now researchers at Drexel University in Philadelphia have demonstrated that it's possible to use techniques borrowed from the chip-making industry to make thin-film carbon ultracapacitors that store three times as much energy by volume as conventional ultracapacitor materials. While that is not as much as batteries, the thin-film ultracapacitors could operate without ever being replaced.
Big Energy Storage in Thin Films
Energy storage devices called superapacitors can be recharged many more times than batteries, but the total amount of energy they can store is limited. This means that the devices are useful for providing intense bursts of power to supplement batteries but less so for applications that require steady power over a long period, such as running a laptop or an engine.
Now researchers at Drexel University in Philadelphia have demonstrated that it's possible to use techniques borrowed from the chip-making industry to make thin-film carbon ultracapacitors that store three times as much energy by volume as conventional ultracapacitor materials. While that is not as much as batteries, the thin-film ultracapacitors could operate without ever being replaced.
These charge-storage films could be fabricated directly onto RFID chips and the chips used in digital watches, where they would take up less space than a conventional battery. They could also be fabricated on the backside of solar cells in both portable devices and rooftop installations, to store power generated during the day for use after sundown. The materials have been licensed by Pennsylvania startup Y-Carbon.
An ultracapacitor is "an electrical energy source that has virtually unlimited lifetime," says Yury Gogotsi, professor of materials science and engineering at Drexel University in Philadelphia, who led the development of the thin-film ultracapacitors. "It will live longer than any electronic device and never needs to be replaced." While batteries store and release energy in the form of chemical reactions, which cause them to degrade over time, ultracapacitors work by transferring surface charges. This means they can charge and discharge rapidly, and because the electrode materials aren't involved in any chemical reactions, they can be cycled hundreds of thousands of times. Researchers have begun developing thin-film ultracapacitor materials but have had difficulty getting high enough total energy storage using practical fabrication methods, says Gogotsi.
Gogotsi's group uses a high-vacuum method called chemical vapor deposition to create thin films of metal carbides such as titanium carbide on the surface of a silicon wafer. The films are then chlorinated to remove the titanium, leaving behind a porous film of carbon. In each place where a titanium atom was, a small pore is left behind. "The film is like a molecular sponge, where the size of each pore is equal to the size of a single ion," says Gogotsi. This matching means that when used as the charge-storage material in an ultracapacitor, the carbon films can accumulate a large amount of total surface charge. The Drexel researchers complete the device by adding metal electrodes to either surface to carry current into and out of the device and adding a liquid electrolyte to carry the charges. They found that the performance of the device is best when the carbon material is about 50 micrometers thick, about the same as the width of a human hair.
The Drexel researchers first developed this ultracapacitor material a few years ago; today in the journal Science they report the first demonstration of thin films made from it. Conventional ultracapacitors are made from powdered activated carbon. These powders can't be used to make large, thin films because they won't stick to the surface. Other groups have developed printable thin-film ultracapacitors based on carbon nanotubes; Gogotsi says his devices can store more charge.
Gogotsi says there is, in theory, no limit to the size of the films that could be made using these methods, which are used by the solar industry and display industries to make panels as large as nine square meters. Because the carbon films are thin and can be made at temperatures as low as 200 ?C, it might be possible to integrate them with flexible electronics.
Source: http://www.technologyreview.com/
RELATED ITEMS:
Group of american researchers from Drexel University created unique supercapacitors »
Pore Size Reduction Increases Energy Stored In Super Capacitors »
11th International Conference on Frontiers of Polymers and Advanced Materials 22 - 27 May 2011 »
AABC Europe. ECCAP Symposium Large EC Capacitor Technology and Application, June 6-10, 2011 Germany »



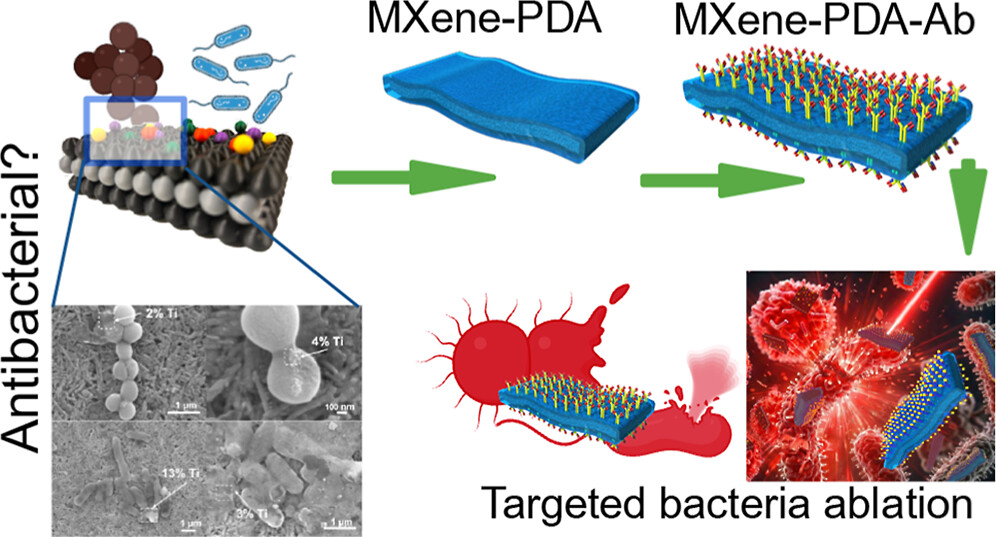 Do MXene nanosheets possess intrinsic antibacterial activity? A systematic study of high-quality Ti-, V-, and Nb-based MXenes reveals negligible inherent antimicrobial effects while highlighting their strong potential for targeted photothermal antibacterial therapy.
Do MXene nanosheets possess intrinsic antibacterial activity? A systematic study of high-quality Ti-, V-, and Nb-based MXenes reveals negligible inherent antimicrobial effects while highlighting their strong potential for targeted photothermal antibacterial therapy. Highlights
Highlights We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development.
We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development. Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments.
Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments. Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
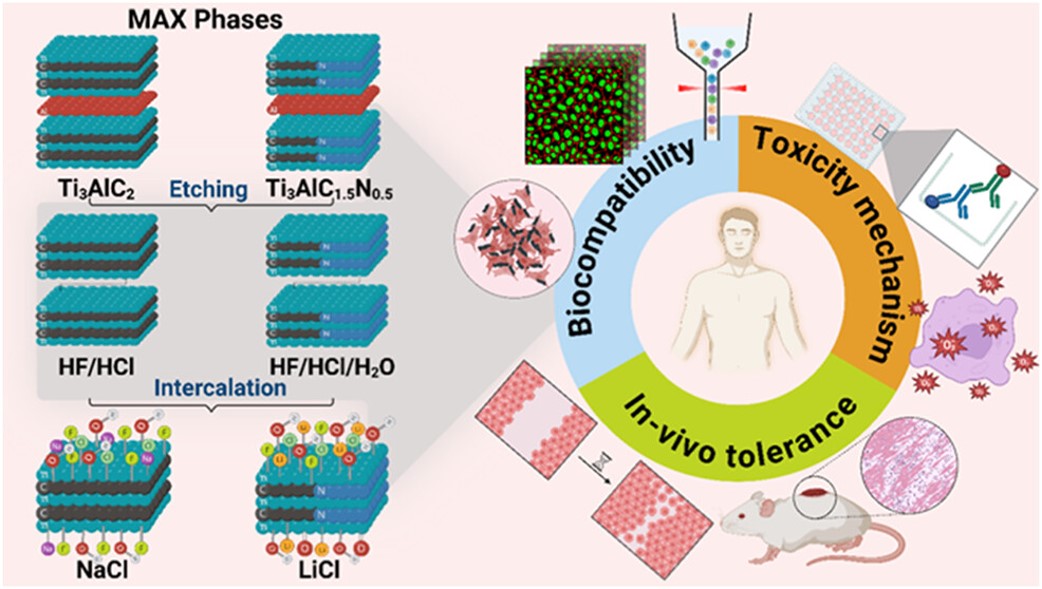 MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.
MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.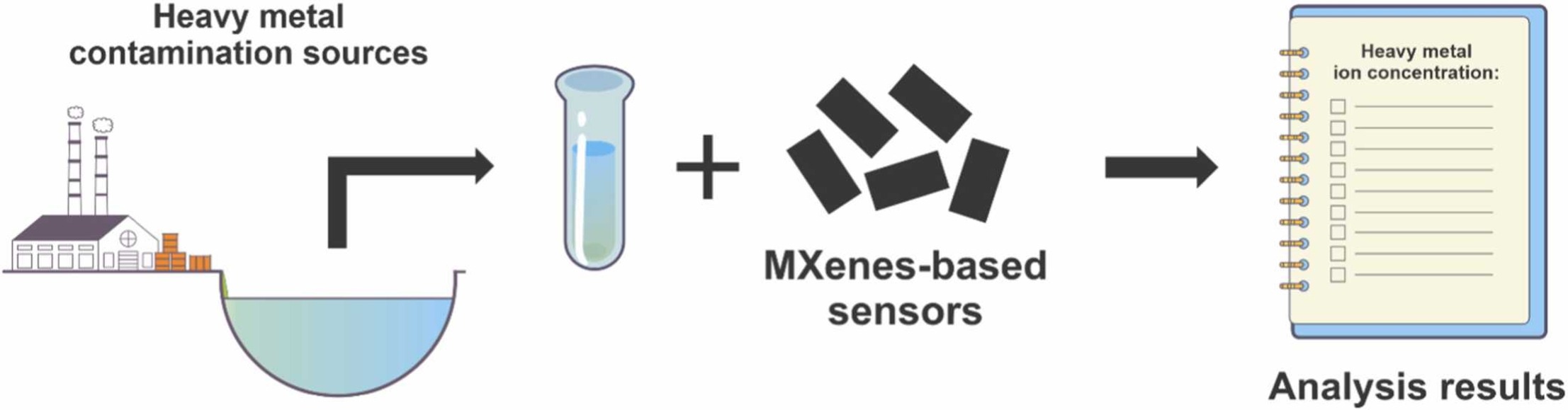 An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
 Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme.
Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme. Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved!
Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved! Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!
Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!  Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!
Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!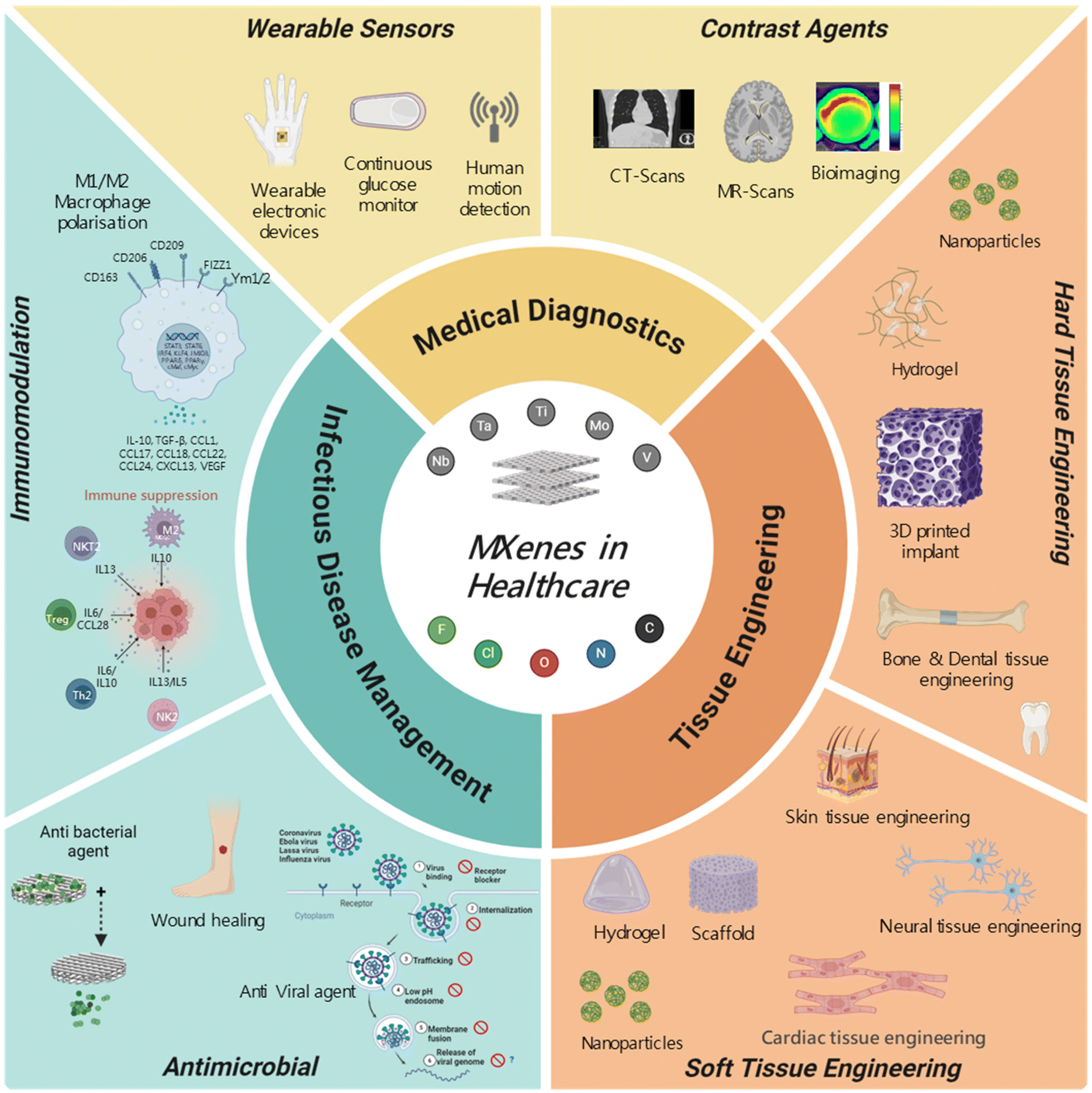 We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.
We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.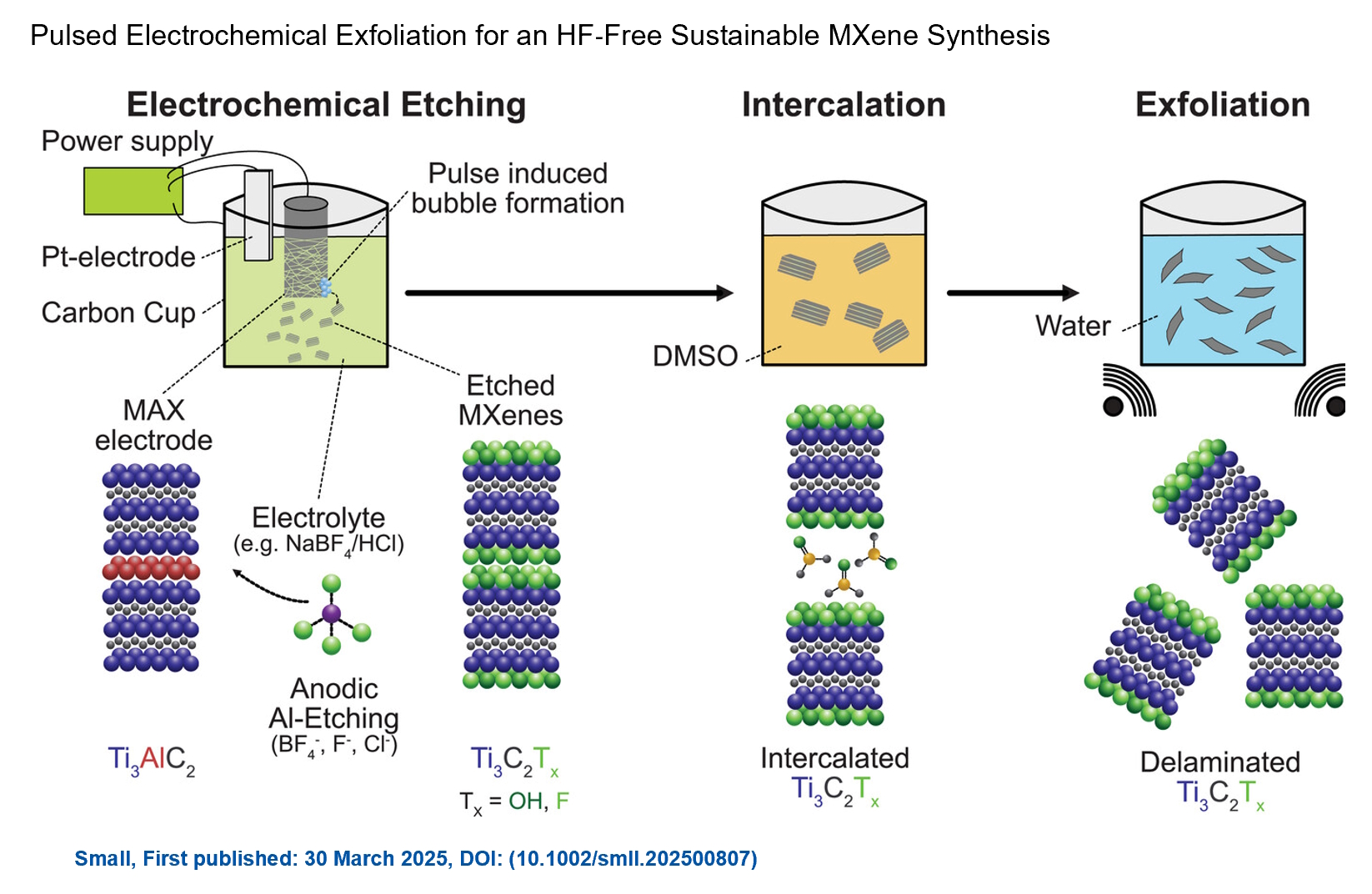 Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.
Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.