MXenes in healthcare: transformative applications and challenges in medical diagnostics and therapeutics
Keshav Narayan Alagarsamy a, Leena Regi Saleth a, Kateryna Diedkova bc, Veronika Zahorodna d, Oleksiy Gogotsi cd, Maksym Pogorielov bc and Sanjiv Dhingra *a
a Institute of Cardiovascular Sciences, St Boniface Hospital Albrechtsen Research Centre, Department of Physiology and Pathophysiology, Max Rady College of Medicine, Rady Faculty of Health Sciences, Biomedical Engineering Program, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, Manitoba R2H 2A6, Canada.
b Institute of Atomic Physics and Spectroscopy, University of Latvia, Jelgavas iela 3, Riga, Latvia LV-1004
c Biomedical Research Center, Sumy State University, Kharkivska street 116, Sumy, Ukraine 40007
d Materials Research Center, 19/33A Yaroslaviv Val/O.Honchara str, Kyiv, 01034, Ukraine
Abstract
MXenes, a novel class of two-dimensional transition metal carbides, exhibit exceptional physicochemical properties that make them highly promising for biomedical applications. Their application has been explored in bioinstrumentation, tissue engineering, and infectious disease management. In bioinstrumentation, MXenes enhance the sensitivity and response time of wearable sensors, including piezoresistive, electrochemical, and electrophysiological sensors. They also function effectively as contrast agents in MRI and CT imaging for cancer diagnostics and therapy. In tissue engineering, MXenes contribute to both hard and soft tissue regeneration, playing a key role in neural, cardiac, skin and bone repair. Additionally, they offer innovative solutions in combating infectious and inflammatory diseases by facilitating antimicrobial surfaces and immune modulation.
Despite their potential, several challenges hinder the clinical translation of MXene-based technologies. Issues related to synthesis, scalability, biocompatibility, and long-term safety must be addressed to ensure their practical implementation in medical applications. This review provides a comprehensive overview of MXenes in next-generation medical diagnostics, including the role they play in wearable sensors and imaging contrast agents. It further explores their applications in tissue engineering and infectious disease management, highlighting their antimicrobial and immunomodulatory properties. Finally, we discuss the key barriers to clinical translation and propose strategies for overcoming these limitations. This review aims to bridge current advancements with future opportunities for integration of MXenes in healthcare.
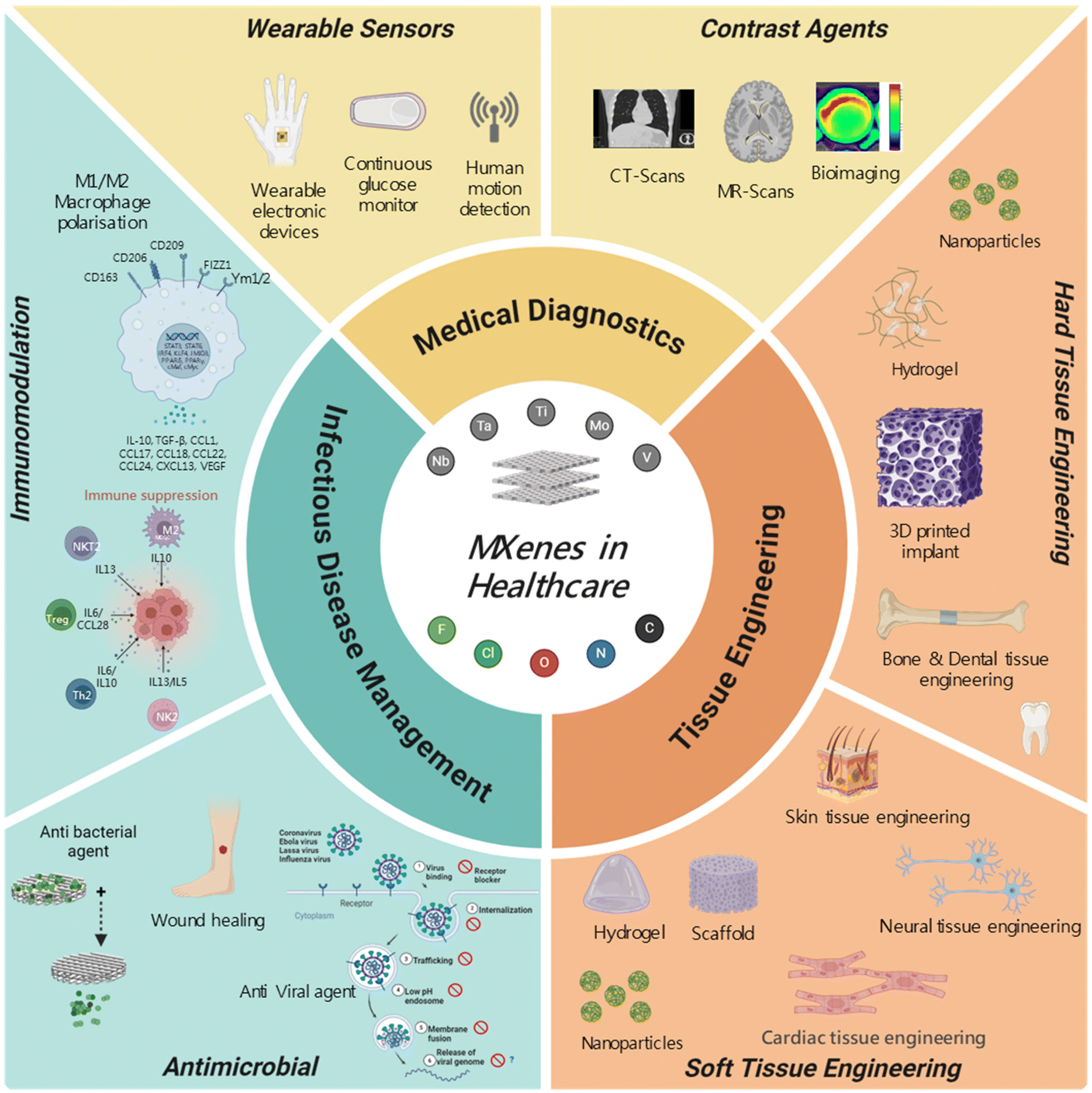
MXenes have surfaced as highly advantageous materials for biomedical applications, especially in the realms of drug delivery, biosensing, tissue engineering, and oncological treatment. The distinctive physicochemical characteristics exhibited by MXenes, including elevated electrical conductivity, extensive surface area, and adjustable surface chemistry, render them exceedingly adaptable. Nevertheless, notwithstanding their promising capabilities, MXenes encounter numerous obstacles that necessitate resolution for their effective clinical application. These obstacles encompass inadequate physiological stability, apprehensions regarding cytotoxicity, challenges related to scalability, susceptibility to oxidative degradation, and implications for environmental sustainability. One of the primary limitations of MXenes in biomedical applications is their poor stability in physiological environments. Their high decomposition rate can reduce their effectiveness in drug delivery and limit their long-term performance in biological systems. A promising approach for enhancing stability is the formation of MXene-based composites with other two-dimensional materials, such as graphene or transition metal dichalcogenides. These hybrid materials have demonstrated improved drug release profiles and prolonged delivery in preclinical studies. Additionally, surface functionalization with functional groups such as hydroxyl (–OH) and oxygen-containing moieties can improve MXene stability and facilitate better drug loading and controlled release.
Another critical challenge is the scalability of MXene synthesis. Current methods, such as chemical exfoliation, involve complex and expensive procedures that limit large-scale production. The development of cost-effective synthesis approaches, such as fluoride-free hydrothermal synthesis, can enhance the commercial viability of MXenes. Furthermore, advancements in automated and high-yield production techniques will be necessary to make MXenes more accessible for biomedical applications. Addressing scalability issues will be a key factor in accelerating their transition from laboratory research to clinical applications.
While MXenes are generally considered biocompatible, their cytotoxicity and long-term biosafety remain concerns. Some studies have reported potential toxicity at higher concentrations or in specific biological environments. To ensure their safe use in clinical applications, rigorous in vitro and in vivo toxicity studies are essential. Standardized testing protocols must be developed to facilitate consistent evaluation across different studies and research groups. Additionally, surface modifications using biocompatible coatings with MXenes, such as polyethylene glycol or silicon dioxide, can help mitigate toxicity concerns, enhance biosafety and reduce their oxidation.
Pharmacokinetics also poses a significant challenge for MXene-based drug delivery systems. Poor targeting efficiency and limited circulation time in the body can reduce their therapeutic effectiveness. To address this, future research should focus on developing targeted drug delivery systems by functionalizing MXenes with targeting ligands, such as antibodies, peptides, or aptamers. Additionally, optimizing MXene size, surface charge, and hydrophilicity can improve their biodistribution and circulation time, making them more effective in drug delivery and cancer therapy.
The environmental impact of MXene synthesis and disposal is another area of concern. Traditional synthesis methods rely on strong acids and high temperatures, which generate harmful byproducts. Additionally, the potential release of MXene nanoparticles into the environment poses risks that have not yet been fully explored. Future research should focus on developing green synthesis methods that minimize toxic waste and reduce environmental hazards. Additionally, studies on MXene biodegradability and long-term environmental fate are necessary to ensure their safe use and disposal.
Regulatory challenges also present a major hurdle for the clinical translation of MXene-based technologies. Currently, standardized safety and efficacy guidelines for MXenes in biomedical applications are lacking. Establishing regulatory frameworks and toxicity testing protocols will be crucial for obtaining clinical approval. Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and regulatory agencies will play a pivotal role in addressing these challenges and accelerating the integration of MXenes into clinical practice.
In order to overcome these challenges and fully realize the potential of MXenes in advanced medical technologies, scientists, engineers and clinicians must work together as an interdisciplinary team. With continued research and development, MXenes could enact a transformative role in medicine, specifically in tissue engineering, sensor development, and theranostics, contributing to the future of personalized and regenerative medicine.
Read more detailed review: Keshav Narayan Alagarsamy, Leena Regi Saleth, Kateryna Diedkova, Veronika Zahorodna, Oleksiy Gogotsi, Maksym Pogorielov and Sanjiv Dhingra. MXenes in Healthcare: Transformative Applications and Challenges in Medical Diagnostics and Therapeutics. Nanoscale, 2025, Advance Article. DOI: 10.1039/D4NR04853A



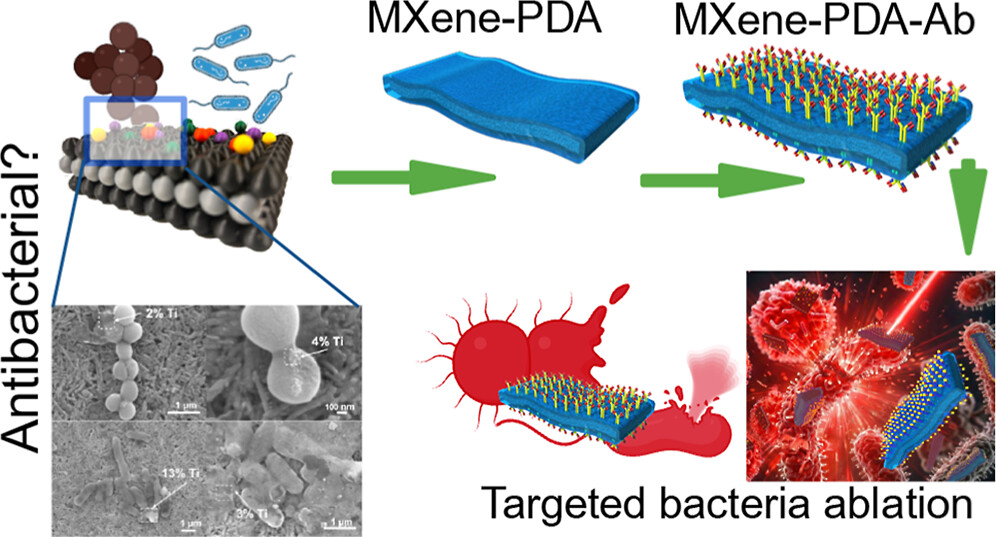 Do MXene nanosheets possess intrinsic antibacterial activity? A systematic study of high-quality Ti-, V-, and Nb-based MXenes reveals negligible inherent antimicrobial effects while highlighting their strong potential for targeted photothermal antibacterial therapy.
Do MXene nanosheets possess intrinsic antibacterial activity? A systematic study of high-quality Ti-, V-, and Nb-based MXenes reveals negligible inherent antimicrobial effects while highlighting their strong potential for targeted photothermal antibacterial therapy. Highlights
Highlights We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development.
We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development. Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments.
Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments. Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
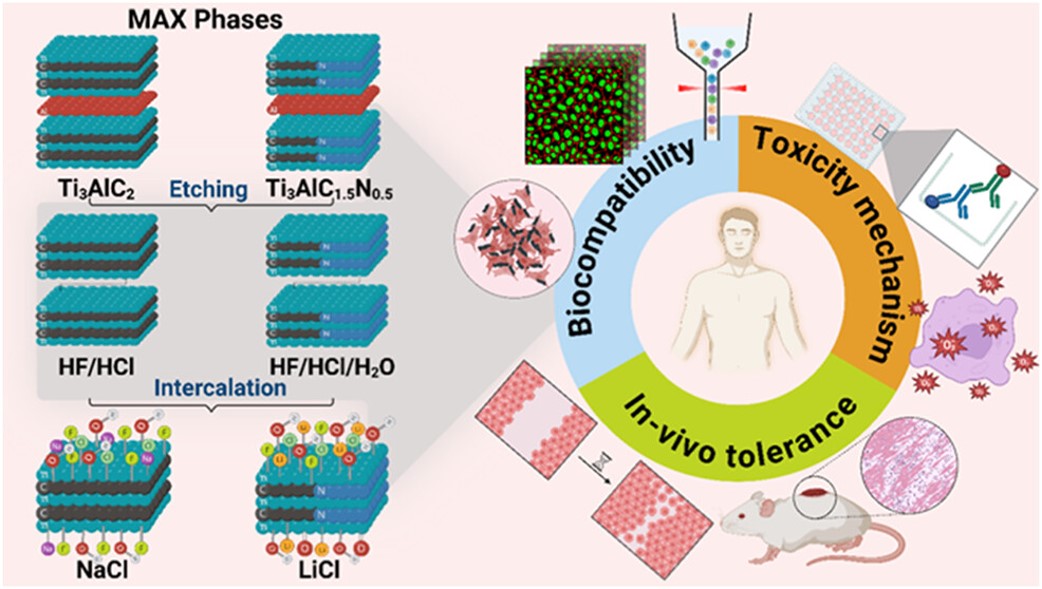 MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.
MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.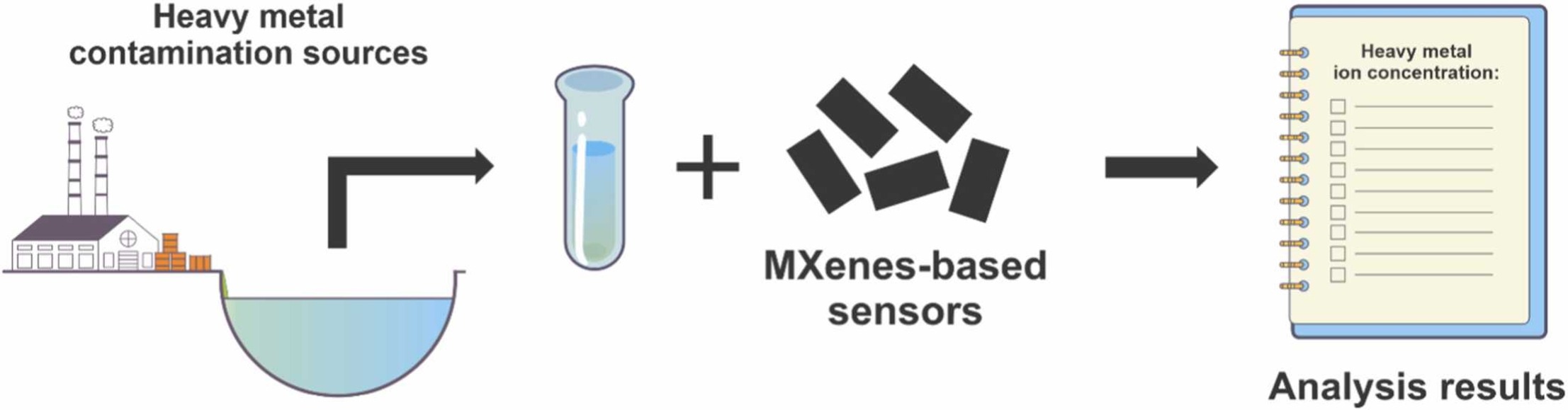 An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
 Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme.
Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme. Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved!
Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved! Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!
Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!  Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!
Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!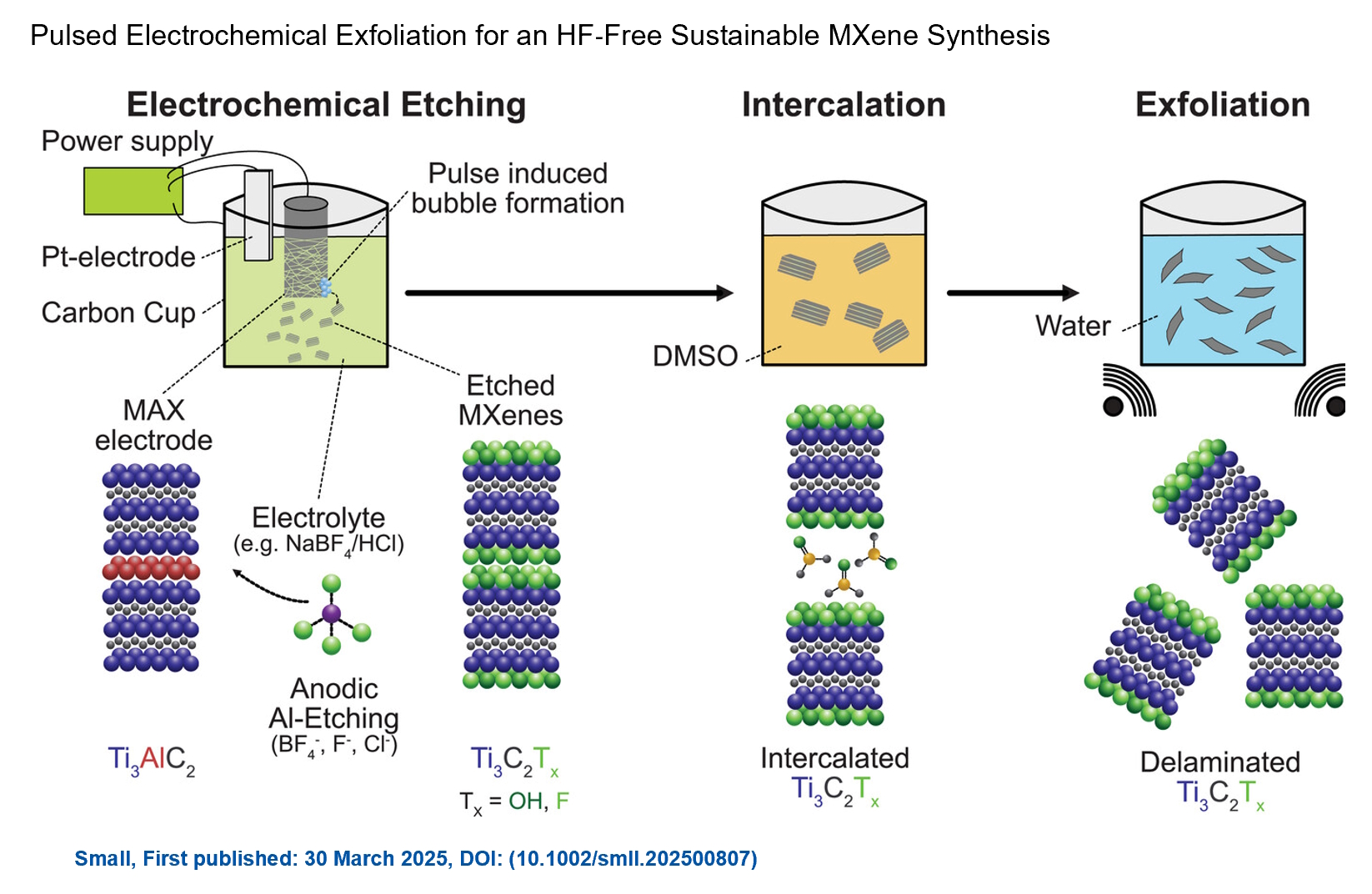 Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.
Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.