
| Rus | Eng |
MRC team members Dr. Oleksiy Gogotsi, Veronika Zahorodna, Dr. Iryna Roslyk visited MXene Confrence 2022. This 2nd international MXene conference at Drexel University, August 1-3, 2022, put major MXene discoveries, including their record-breaking electrical conductivity, electromagnetic interference shielding capability, electrochemical capacitance, light-to-heat conversion, and other properties, into perspective; identifies areas of basic research; familiarizes a diverse student body, as well as scientists and engineers, with these novel 2D materials; and brings the technological potential of MXenes to the attention of industries, federal and state governments, funding agencies, and decision-makers.
Over the course of the three full days, the conference brought together MXene researchers and collaborators in the areas of energy storage and generation, electromagnetic interference shielding, antennas, transparent conductors, gas and pressure sensors, water purification, gas separation membranes, photo- and electrocatalysis, medicine, and plasmonics among many others, to identify basic research problems and the future technologies that will use MXenes to address current global challenges.
MXene Conference Day 1
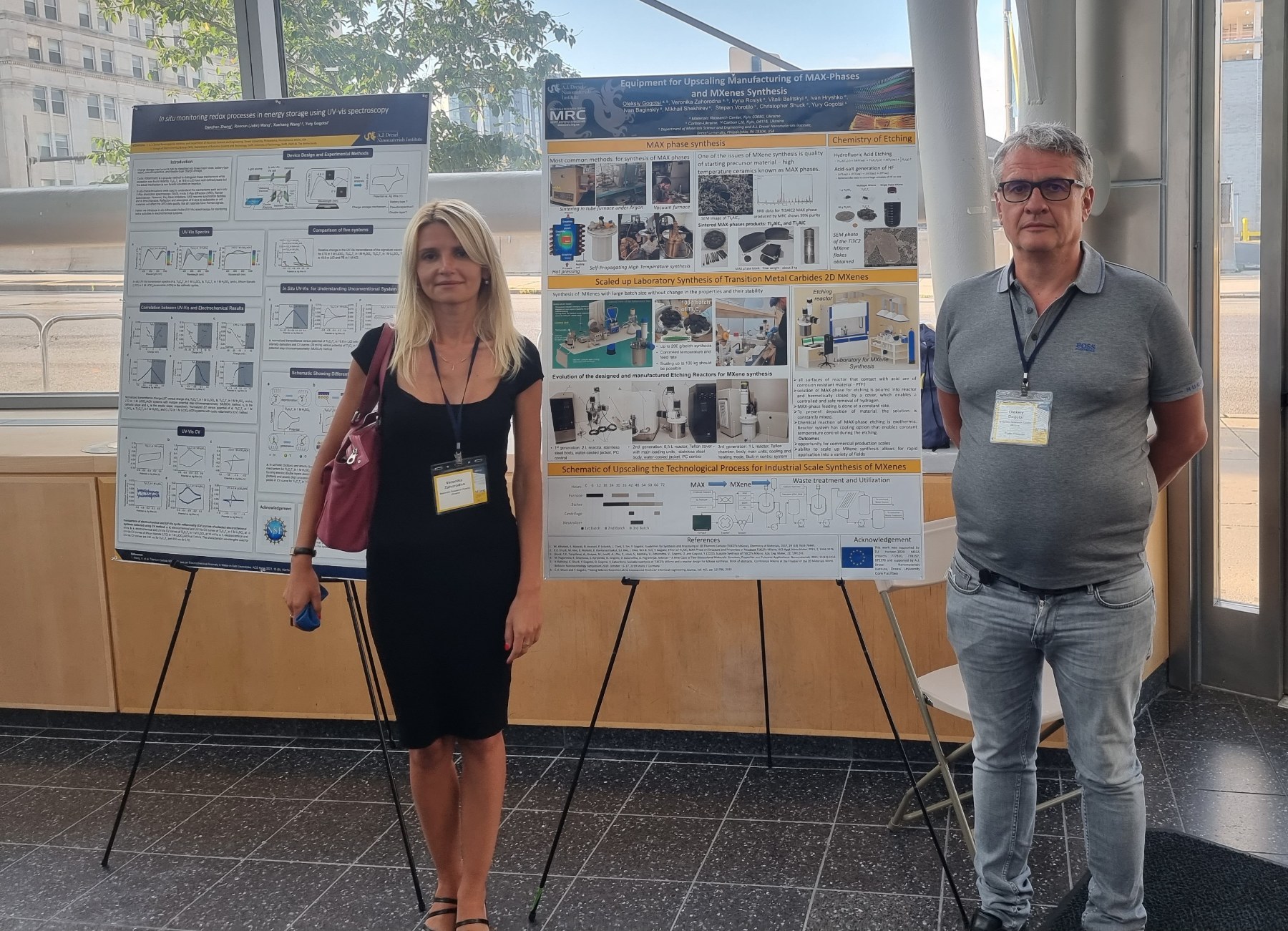
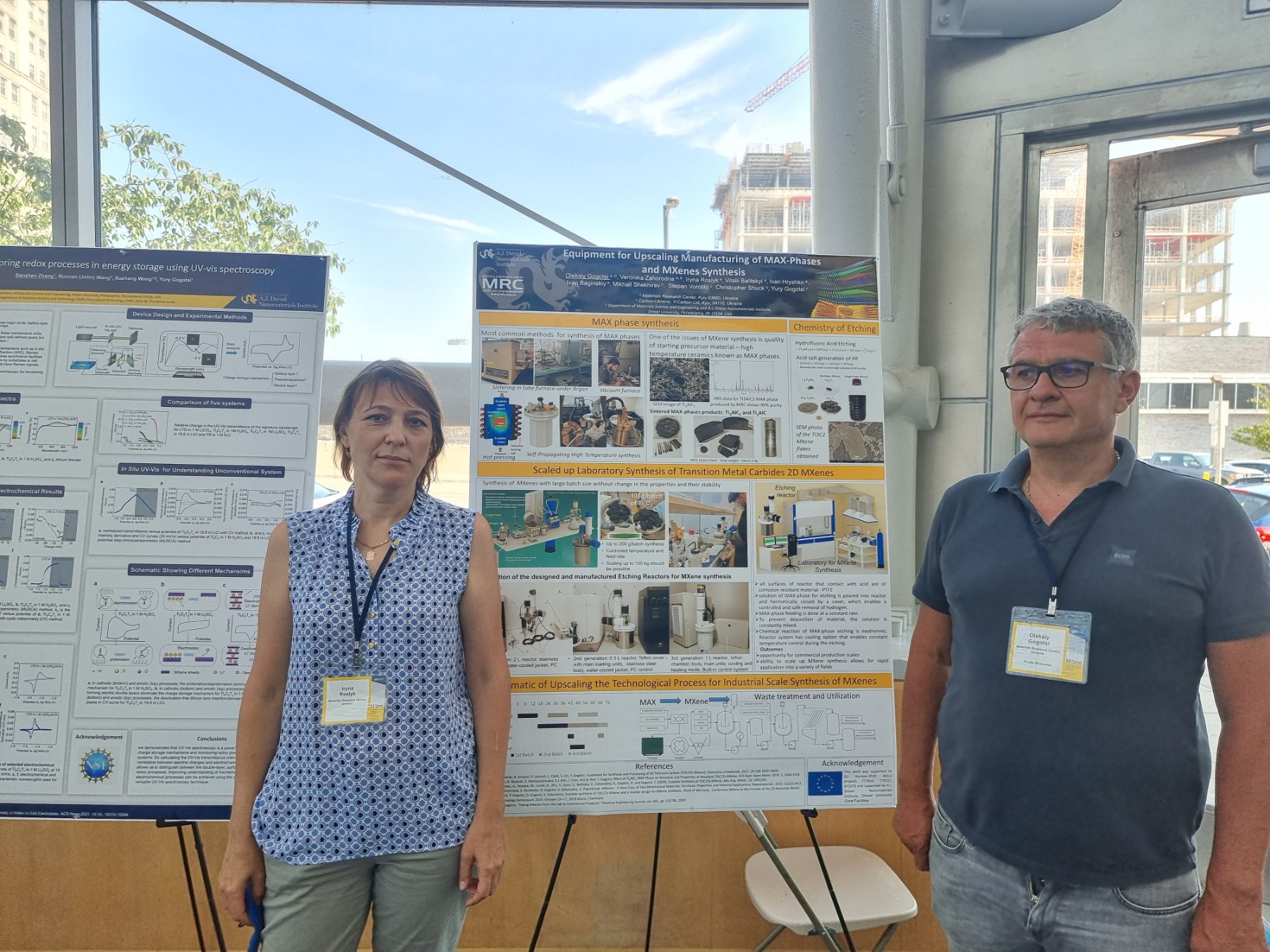
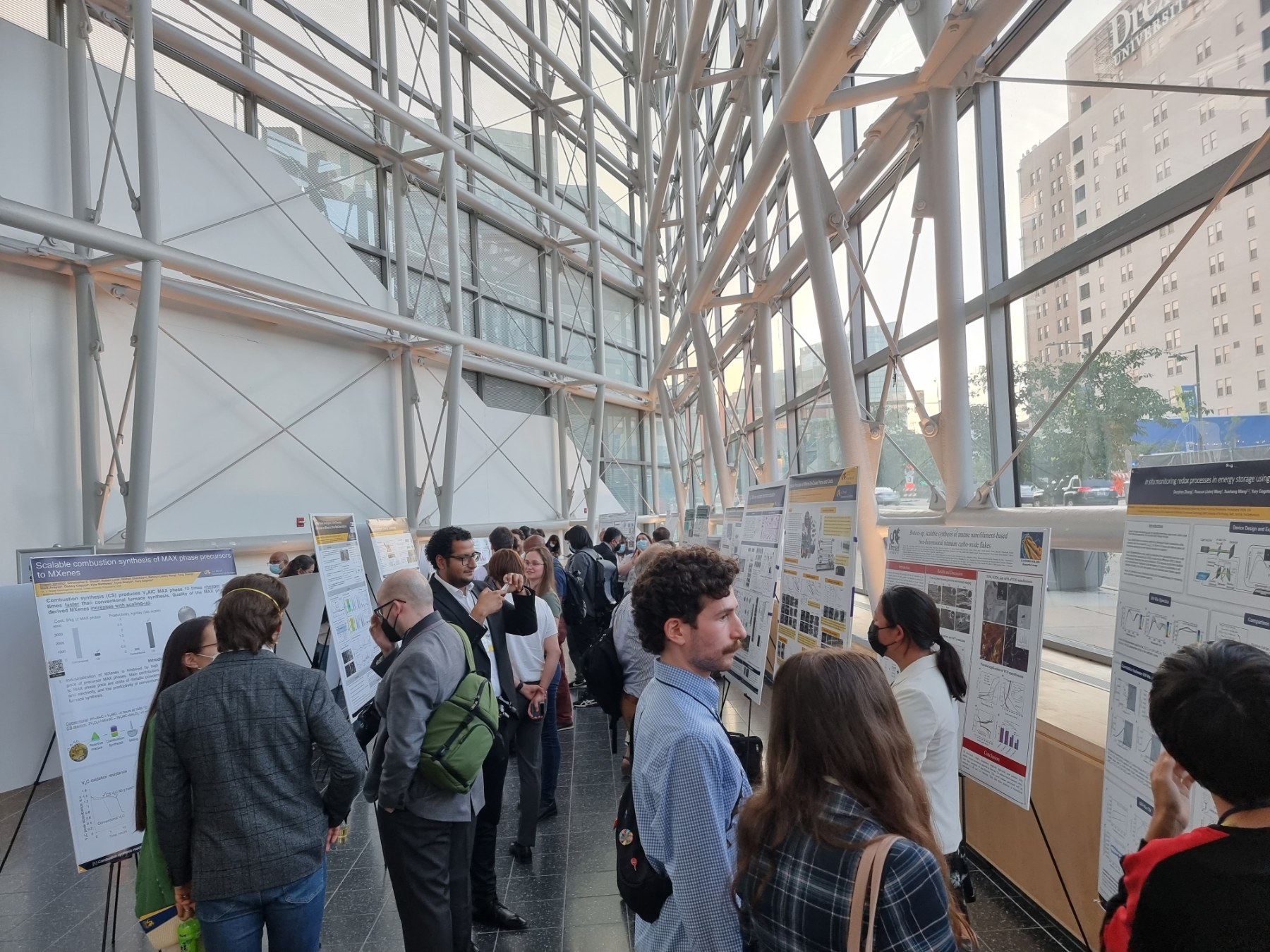 Team members from Materials Research Center Dr. Oleksiy Gogotsi and Veronika Zahorodna and Dr. Iryna Roslyk also took part in MXene 2022 conference promoting their research and engineering activities at poster session. They presented our collaborative work with Drexel Nanomaterial group:
Team members from Materials Research Center Dr. Oleksiy Gogotsi and Veronika Zahorodna and Dr. Iryna Roslyk also took part in MXene 2022 conference promoting their research and engineering activities at poster session. They presented our collaborative work with Drexel Nanomaterial group:
Veronika Zahorodna, Oleksiy Gogotsi, Vitalii Balitskyi, Ivan Baginskiy, Veronika Zahorodna, Iryna Roslyk, Chris Shuck, Mikhail Shekhirev, Stepan Vorotylo, Yury Gogotsi, Equipment for upscaling manufacturing of MAX phases and MXenes synthesis. 2nd International MXene Conference, Drexel University, Philadelphia, USA, Aug. 1–3, 2022.


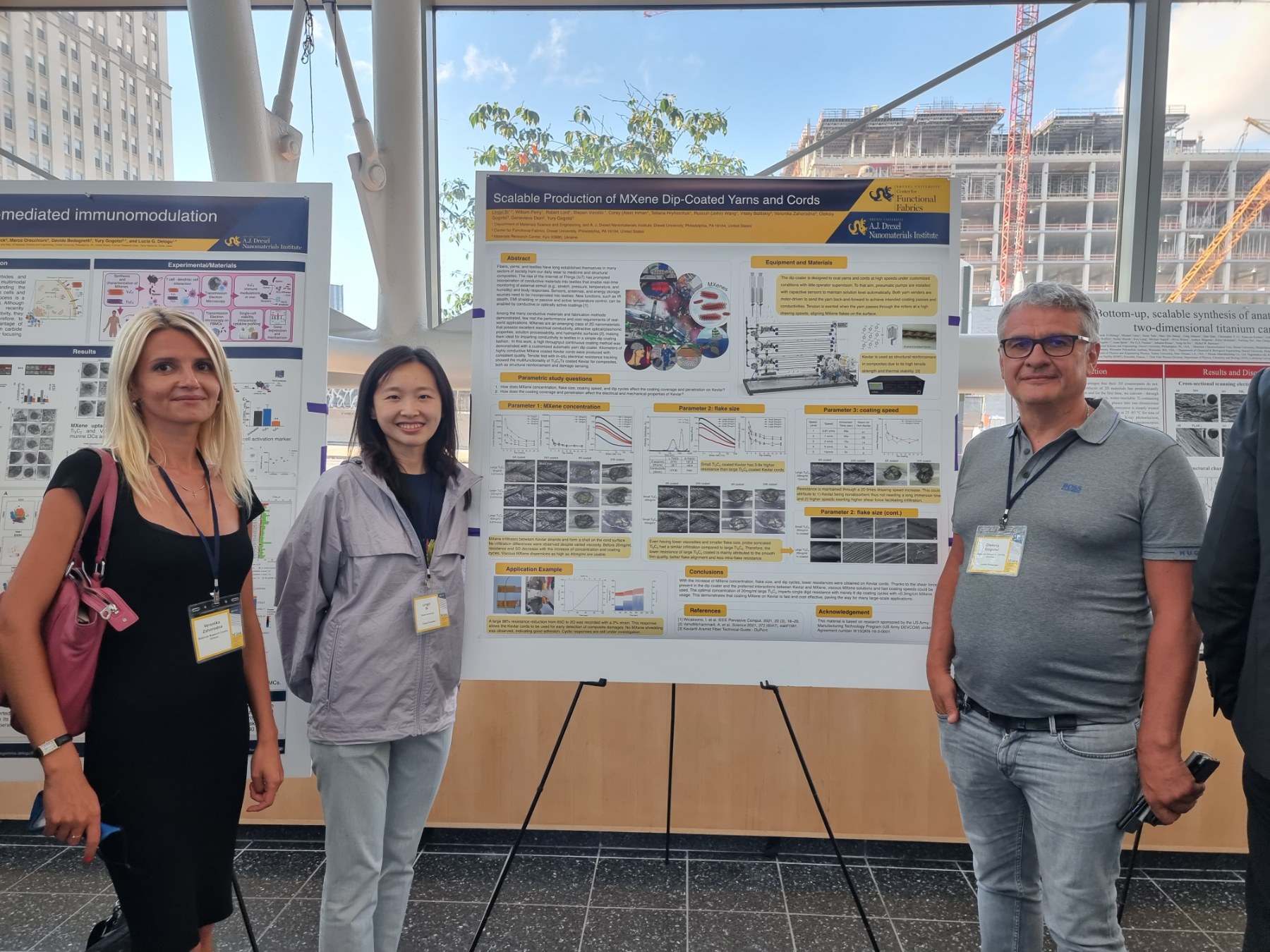
Also at the conference was presented a research work on Scalable Production of MXene Dip-Coated Yarns and Cord by Lingyi Bi from Drexel University, with the coauthors from MRC, showing the research works based on the MXene Yarn coating machine designed, developed and manufactured by MRC team. That poster was recognized by conference comettee as one of the best works presented within the conference. Our congratulations to Lingyi Bi from Drexel Nanomaterils Group!
Lingyi Bi, William Perry, Robert Lord, Stepan Vorotilo, Corey (Alex) Inman, Tetiana Hryhorchuk, Ruocun(John) Wang, Citalii Balitskyi, Veronika Zahorodna, Oleksoy Gogotsi, Genevieve Dion, Yury Gogotsi, Scalable Production of MXene Dip-Coated Yarns and Cord. 2nd International MXene Conference, Drexel University, Philadelphia, USA, Aug. 1–3, 2022.

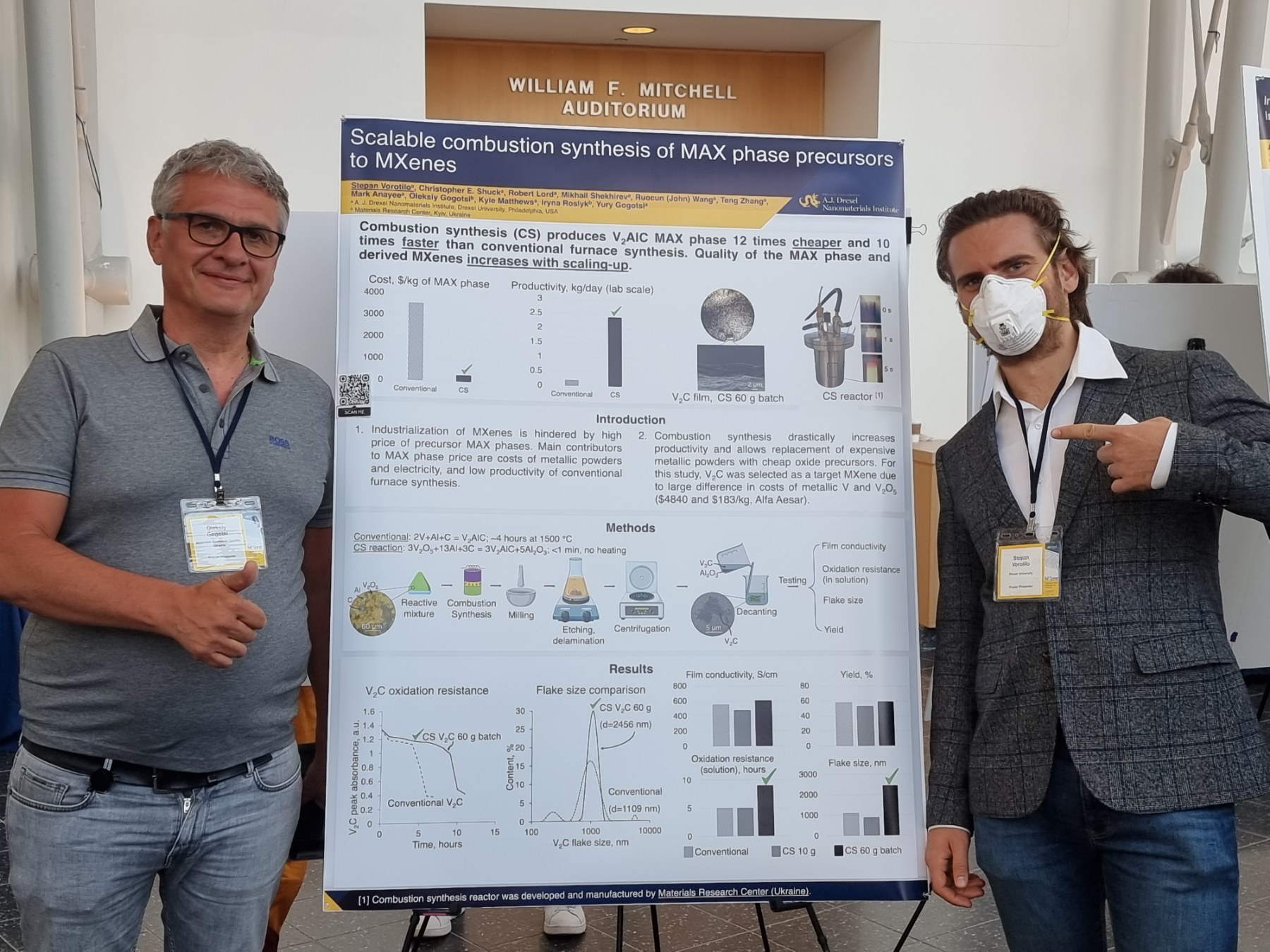
Dr. Oleksiy Gogotsi (MRC) and Stepan Vorotilo (Drexel University) disussed their colaborative work at Drexel University with reactor for self-propagating high-temperature synthesis, designed, developed and manufactured by MRC team at Kyiv, Ukraine.
Stepan Vorotilo, Christopher Shuck, Robert Lord, Mikhail Shekhirev, Ruocun (John) Wang, Teng Zhang, Mark Anayee, Oleksiy Gogotsi, Kyle Matthewes, Iryna Roslyk, Yury Gogotsi, Scalable combustion synthesis of MAX phase precursors to MXenes. 2nd International MXene Conference, Drexel University, Philadelphia, USA, Aug. 1–3, 2022.

MXene Conference Day 2
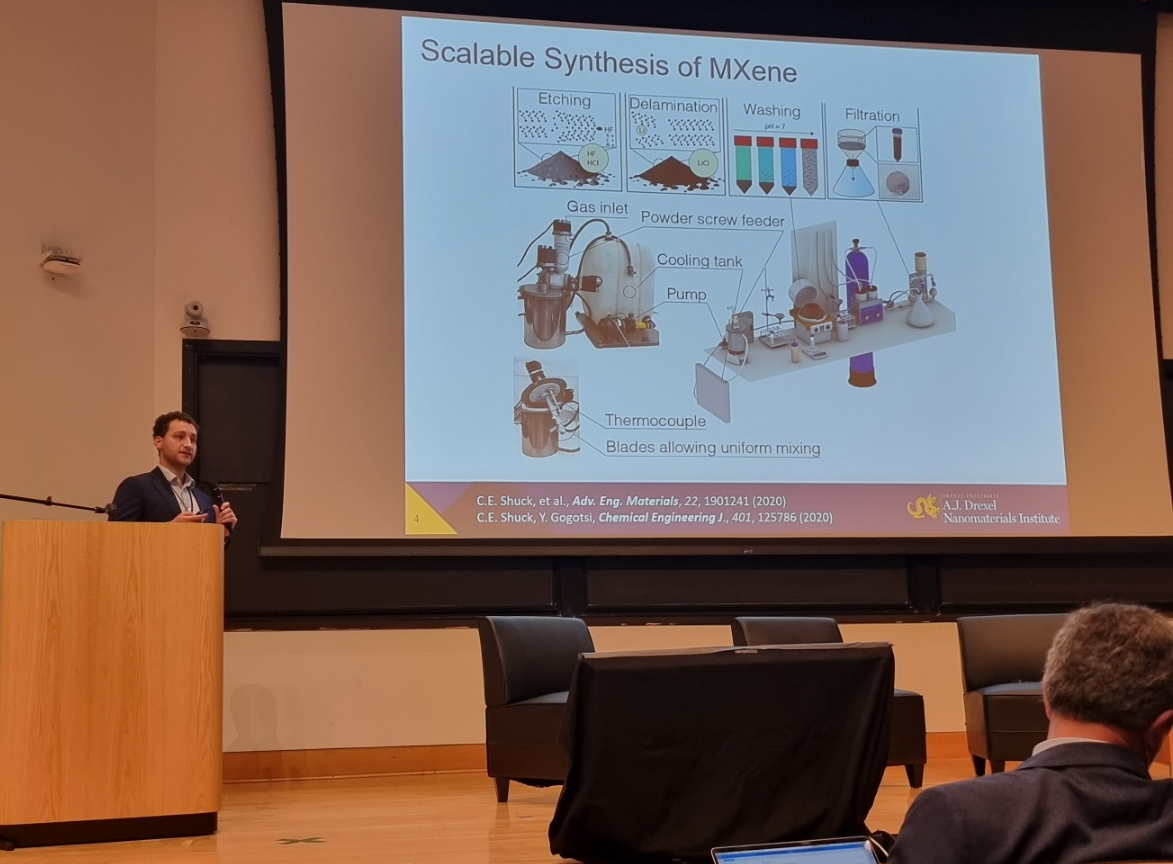
Dr. Christopher E. Shuck, research assistant professor at the A.J. Drexel Nanomaterials Institute, Drexel University gave a plenary lecture on Scalable Synthesis of Tı3C2Tx MXene. His lecture also included slides divided to scaled up MXene sythesis using laboratory etching reactor, MXene yarn coating machine for production of MXene fiber developed and manufactured by MRC team at Kyiv, Ukraine. 


MXene Confernce Day 3



From recent interview of Prof. Yury Gogotsi to DrexelNOW:
MXenes are about the most transferable technology to come out of Drexel, and they're generating patents and licensing deals. Researchers from Drexel University are studying applications from smart textiles to cancer treatment to kidney dialysis to antennas and electromagnetic shields. There have been companies launched to explore applications for them.
In general, it takes usually between 15 and 25 years for new materials to go from discovery to real-world applications. Always when you make materials in small quantities, it is expensive. Until we have a large amount of cheap but high-quality material, the industry will not start using it. Bridging this gap from lab-scale production to large-scale production is always one of the key challenges for new materials.
Chemical companies will not start producing tons and tons until someone wants to buy it. On the other hand, companies that make new gadgets, like cell phones or smart textiles, won't start large-scale production until they have reliable material suppliers. Still, new materials will eventually get into production if they enable major improvement of existing functions (e.g., charging time of a lithium-ion battery) or enable new functions,such as garments with embedded antennas, energy storage capability, body temperature sensors to provide heat in some areas and cooling in other parts, etc.
Some applications are longer-term. There is a medical device company called Nephria Bio working with MXenes to improve kidney dialysis to eventually develop a wearable kidney so people won't depend on dialysis machines. Making a wearable kidney is a very attractive and important goal, but clearly it takes time. Another key application of MXenes is for electromagnetic shielding, such as to eliminate the irritating noise that happens when you have two microphones near each other. Typically, people use metal screens, but we can prevent interference with film that's virtually invisible and extremely thin. Therefore, such shields can potentially be used in hand-held electronics, Internet-of-Things devices, etc., where size and weight are of importance. Companies, researchers and investors can use MXenes to solve many technological problems.
The goal of the conference is to bring together companies, researchers, investors and doctoral or undergraduate students so they can learn and listen to leading experts in the field and select directions for future research. The conference chairs invited leading experts in the field to speak.
MXene Conference website: https://mxeneconference.coe.drexel.edu/



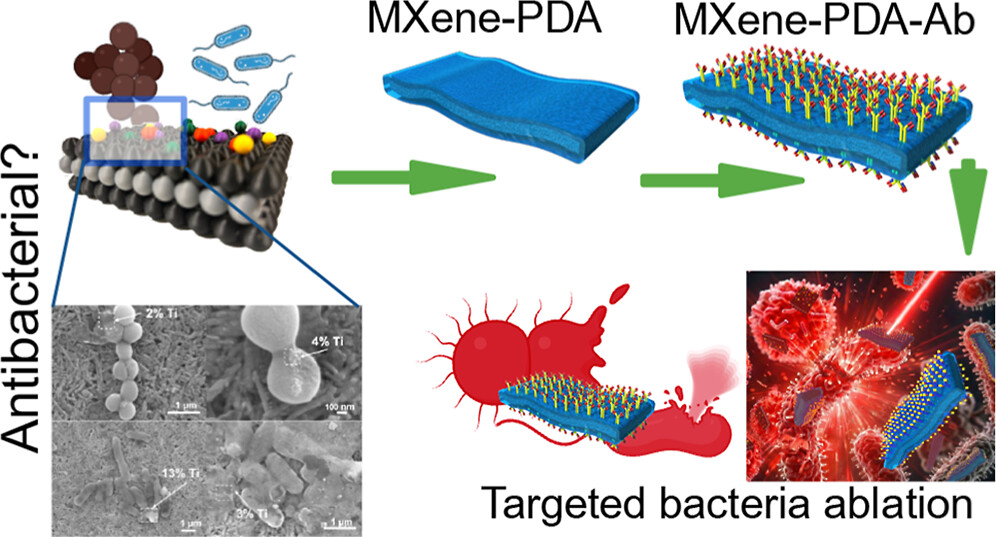 Do MXene nanosheets possess intrinsic antibacterial activity? A systematic study of high-quality Ti-, V-, and Nb-based MXenes reveals negligible inherent antimicrobial effects while highlighting their strong potential for targeted photothermal antibacterial therapy.
Do MXene nanosheets possess intrinsic antibacterial activity? A systematic study of high-quality Ti-, V-, and Nb-based MXenes reveals negligible inherent antimicrobial effects while highlighting their strong potential for targeted photothermal antibacterial therapy. Highlights
Highlights We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development.
We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development. Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments.
Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments. Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.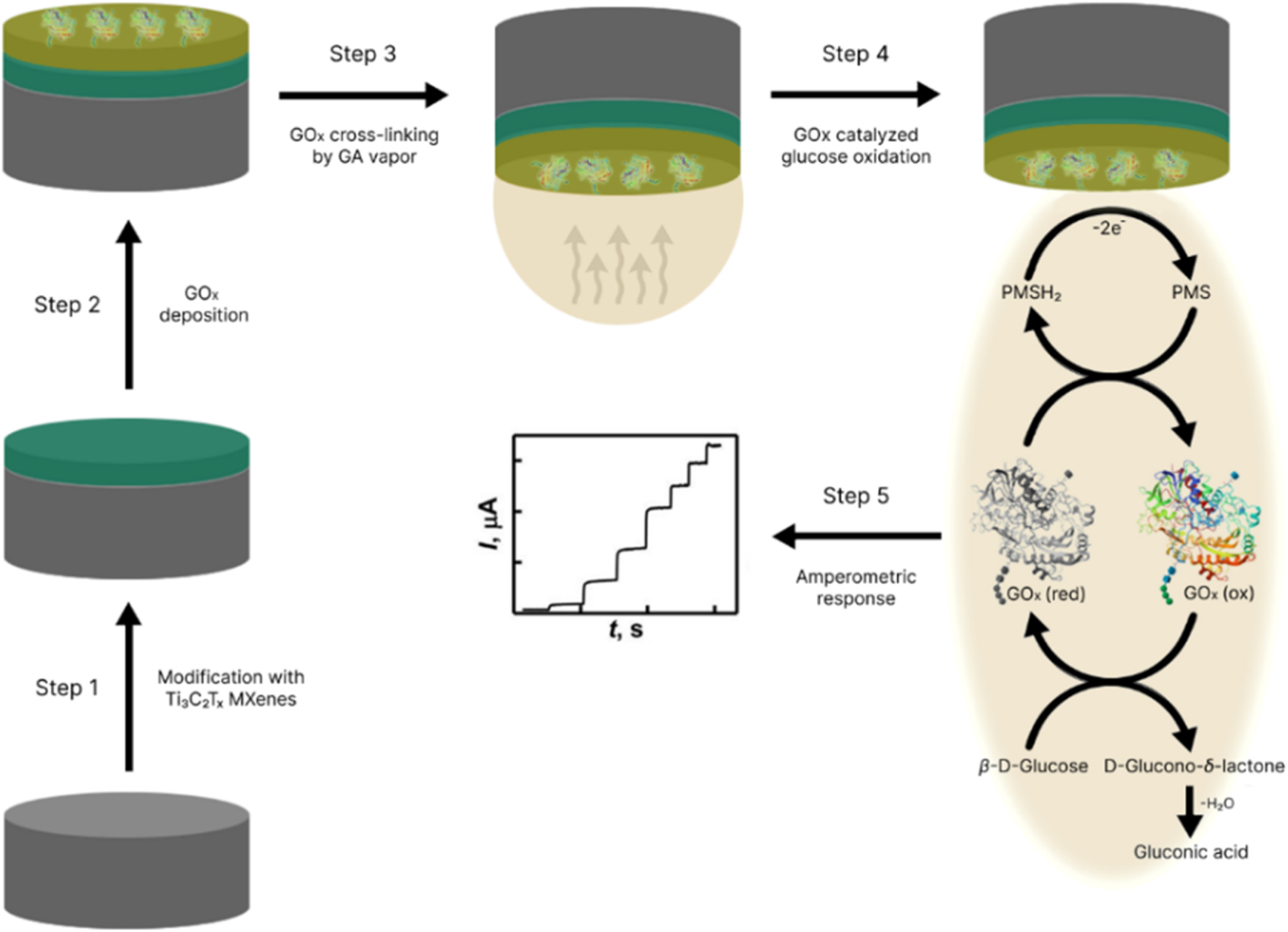
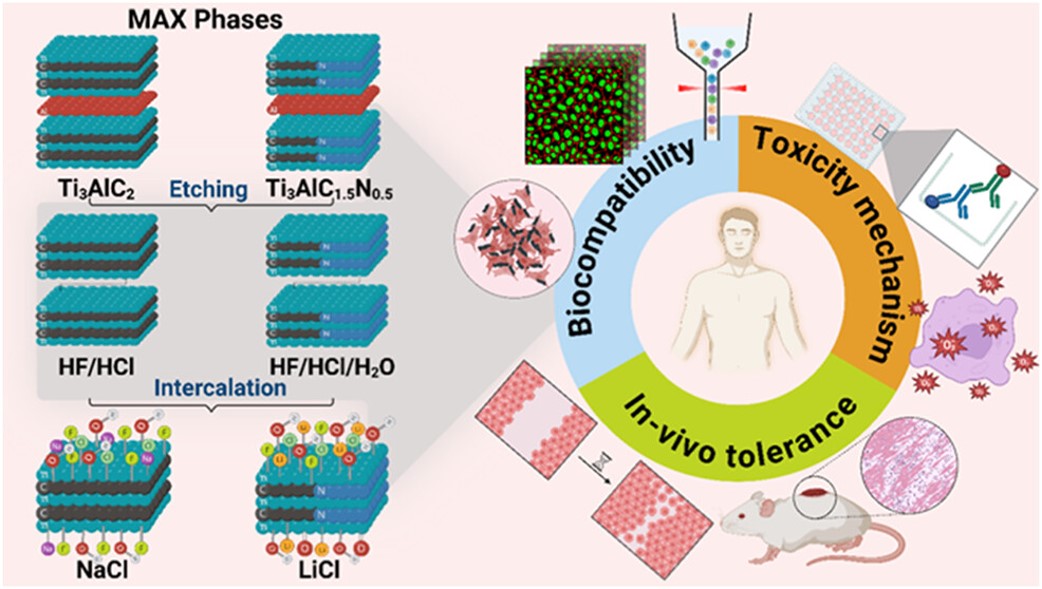 MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.
MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.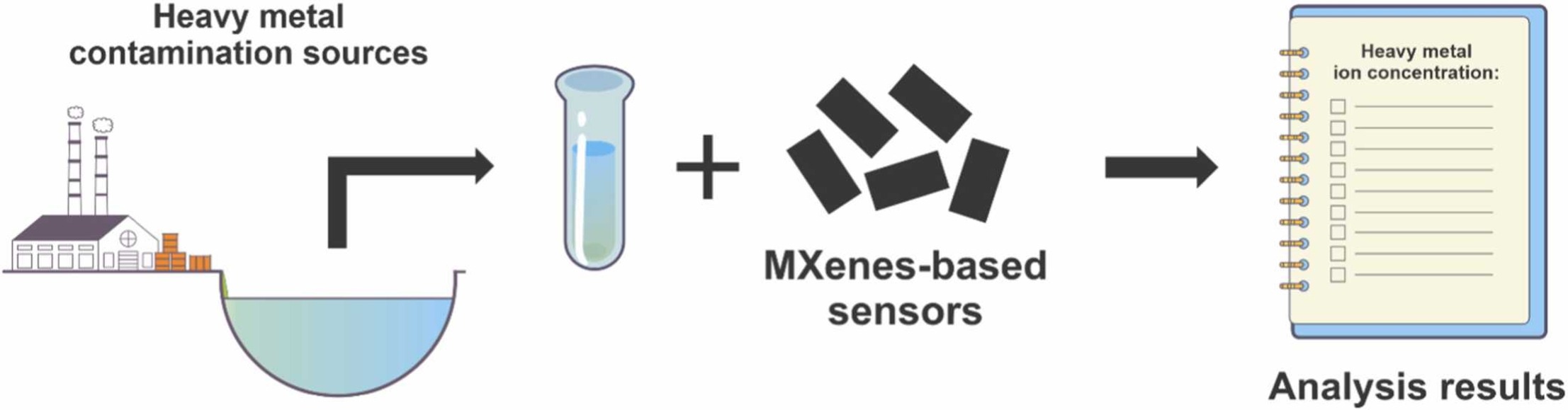 An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
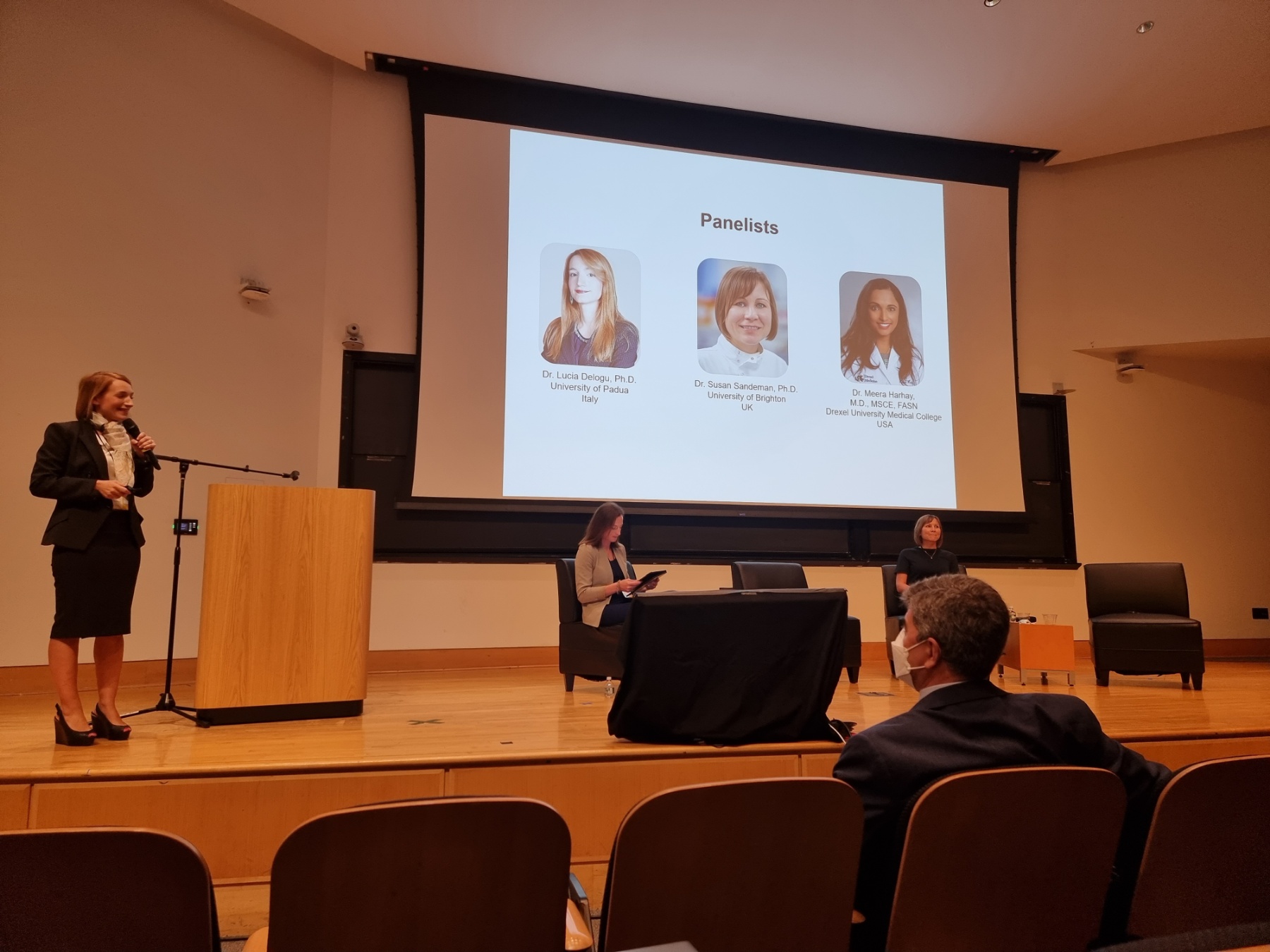
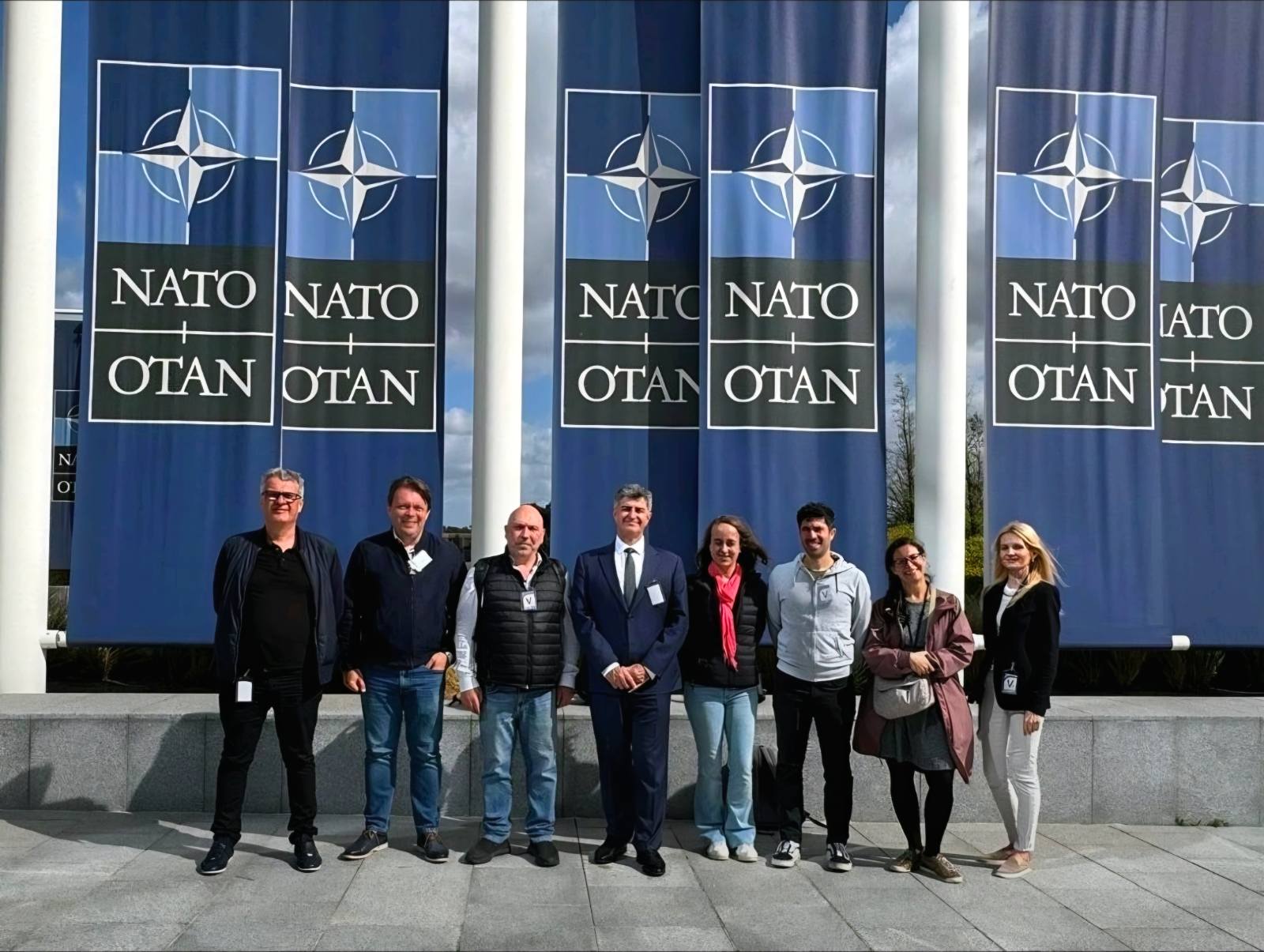 Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme.
Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme. Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved!
Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved!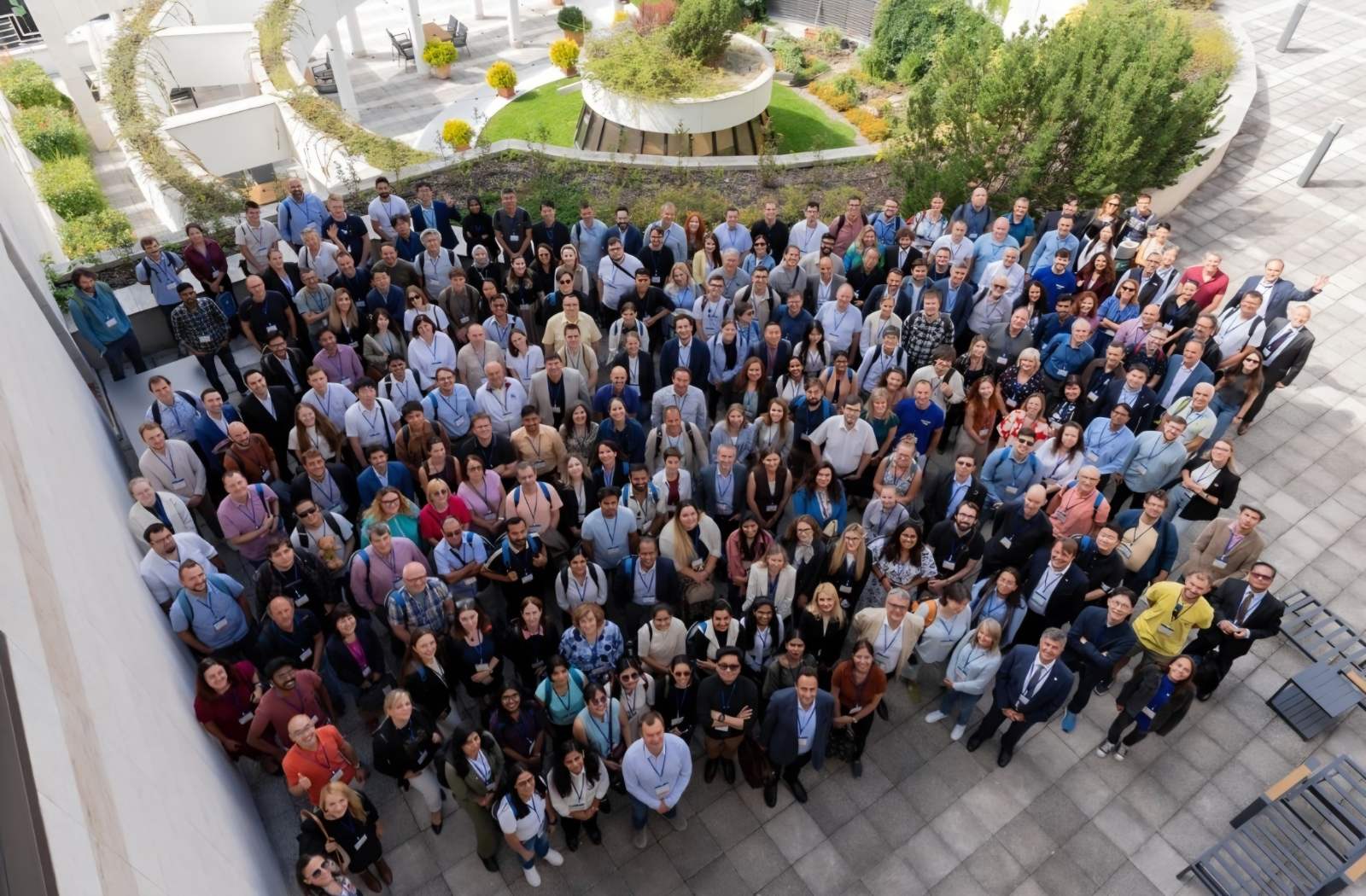 Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!
Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!  Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!
Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!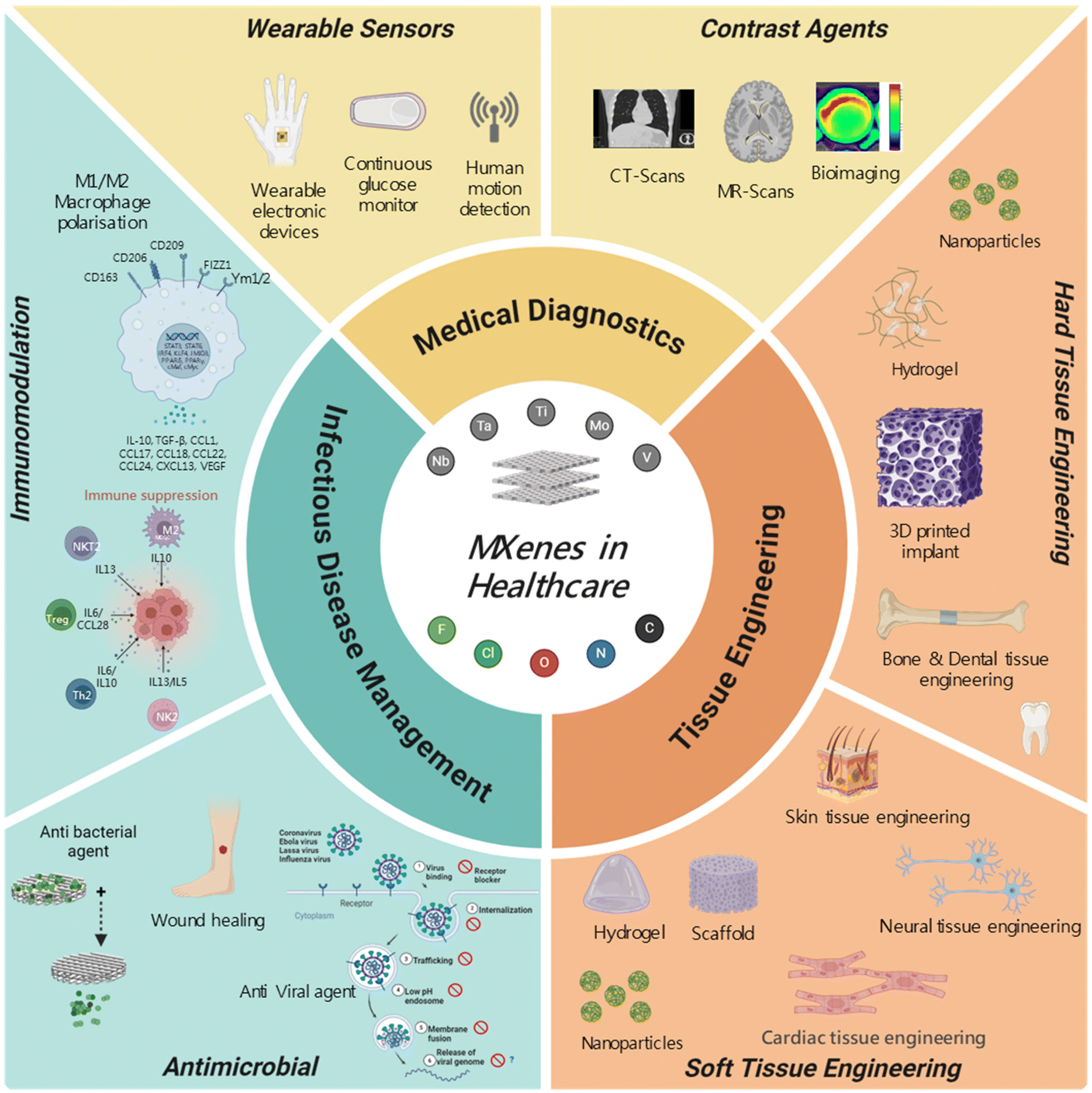 We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.
We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.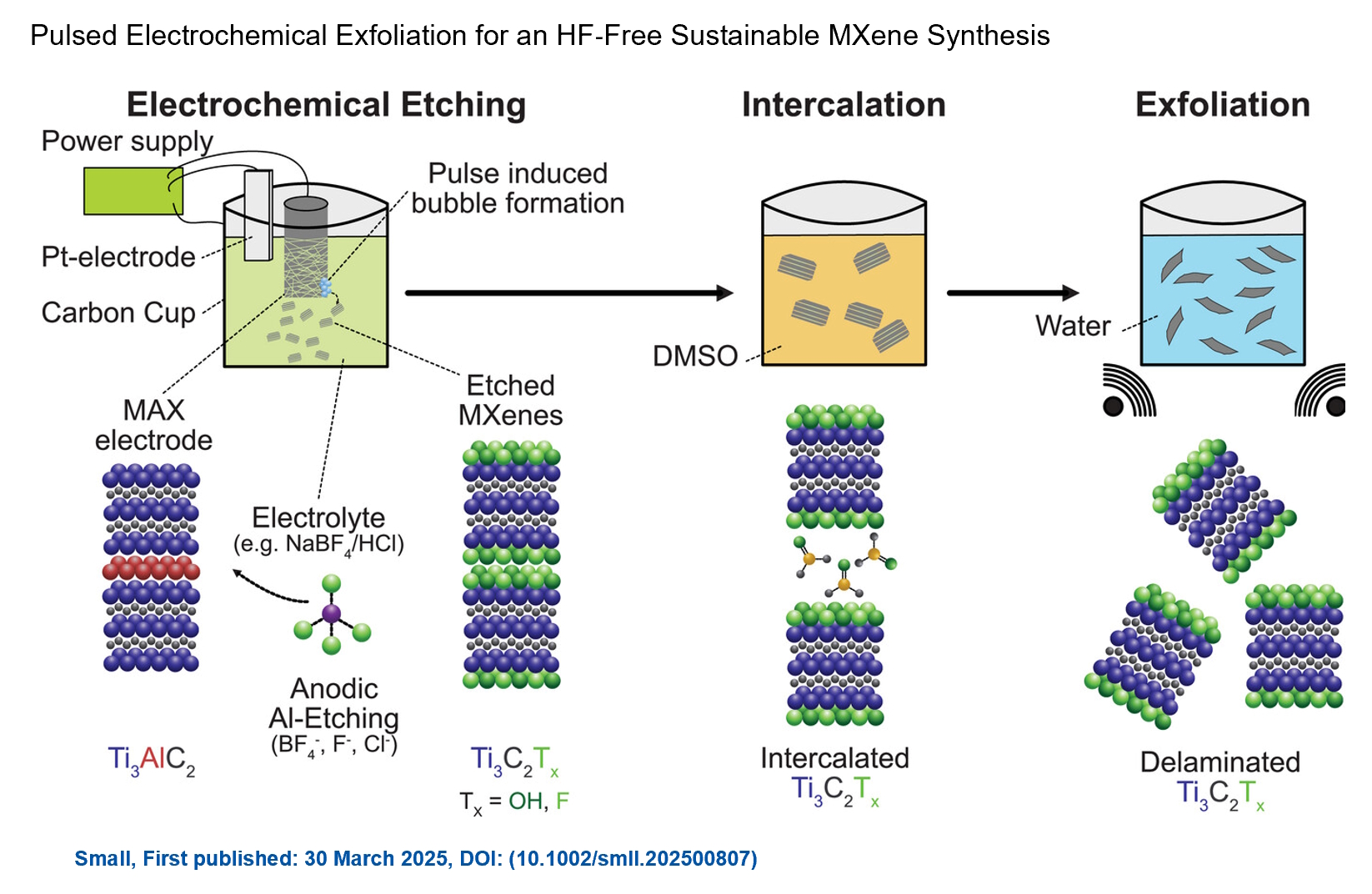 Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.
Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.