Scale-up of MXene Synthesis
O. Gogtosi ab, V. Zahorodna ab, Serhienko A. a, I. Hrysko a, Y. Zozulya a, V. Balitskyi a, M. Seredych c, B. Anasori c, Y. Gogotsi c
a Materials Research Center, Kiev 03680, Ukraine
b National Metallurgical Academy of Ukraine, Dnipro 49600, Ukraine
c A. J. Drexel Nanomaterials Institute, and Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Drexel University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104, United States
Corresponding author: Этот e-mail адрес защищен от спам-ботов, для его просмотра у Вас должен быть включен Javascript
Abstract
The family of two-dimensional (2D) transition metal carbides and nitrides, MXenes, has been expanding rapidly since the discovery of Ti3C2 MXene in 2011 [1]. More than 20 different MXenes have been synthesized, and the structure and properties of numerous other MXenes have been predicted using density functional theory calculations [2].
Two-dimensional (2D) materials with a thickness of a few nanometers or less can be used as single sheets due to their unique properties or as building blocks, to assemble a variety of structures. MXenes properties can be tunable for a large variety of applications [3]that directly lead to their use for electromagnetic shielding [4], transparent conductors, light-to-heat energy conversion, new advanced lasers and photothermal therapy.
Synthesis of MXene typically begins with etching the A-element atomic layers (for example, aluminum) in a MAX phase (for example, Ti3AlC2) with HF solution and/or a mixture of fluoride salts and acids at room temperature or slightly higher temperature. After the etching is finished (complete removal of the A-element layers), washing must be applied to remove residual acid and reaction products (salts) and achieve a safe pH (∼6). After the pH is increased to ∼6, and eventual intercalation of large organic molecules and subsequent delamination completed, the multilayered MXene flakes or single nanosheets can be collected via vacuum-assisted filtration and then dried in vacuum [5].
MXenes can be deposited form solution by spin, spray, or dip coating, painted or printed, or fabricated in a variety of ways. Synthesis conditions used to produce MXenes influence the resulting properties and thus are directly related to the performance of MXenes in their applications [5]. In the laboratory, researchers synthesize MXene in gram quantities, and it is very difficult to repeat the synthesis conditions in order to obtain a material with the same repeatable properties.
For scaling up the laboratory process and to obtain material in larger quantities (up to 200 g per batch) of good quality with repeatable properties, a pilot laboratory line was developed [5]), which allows us to control the etching process and adjust its basic parameters - temperature, mixing speed, recording and storing all necessary data for analysis or to repeat the conditions during subsequent syntheses to obtain a MXene with repeatable properties. In addition, since the acidic etching process is accompanied by the release of heat, a specially developed sealed reactor allows safe and reliable synthesis. The computer control system provides the desired precursor feed rate and the optimal synthesis temperature profile [6].
References
[1] Two-Dimensional Nanocrystals Produced by Exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. M. Naguib, et al., Advanced Materials, 23, 4248 (2011)
[2] Synthesis and Biomedical Applications of 2D Carbides (MXenes). Gogotsi, O. G., Zahorodna, V. V., Balitskiy, V. Y., Zozulya, Y. I., Gogotsi, H. G., Brodnikovskiy, M. P., Gubynskyi, M. V., Fedorov, S. S., Alhabeb, M., Meng, F., Anasori B., Gogotsi, Y. Abstracts Book of 5th International Conference, Nanobiophysics: Fundamental and Applied Aspects, October 2-5, 2017, Kharkiv, Ukraine
[3] Organic-Base-Driven Intercalation and Delamination for the Production of Functionalized Titanium Carbide Nanosheets with Superior Photothermal Therapeutic Performance. J. Xuan, et al., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55, 1 – 7 (2016)
[4] F. Shahzad, M. Alhabeb, C.B. Hatter, B, Anasori, S.M. Hong, C. M. Koo, Y. Gogotsi, Electromagnetic Interference Shielding with 2D Transition Metal Carbides (MXenes), Science, 353 (6304) 1137-1140 (2016)
[5] M. Alhabeb, K. Maleski, B. Anasori, P. Lelyukh, L. Clark, S. Sin, Y. Gogotsi, Guidelines for Synthesis and Processing of 2D Titanium Carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene), Chemistry of Materials, 29 (18) 7633-7644 (2017)
[6] O.O. Honcharuk, V.Y. Balitskiy, R.V. Voron, M.P.Brodnikovskiy, O.G. Gogotsi, V.V. Zahorodna, Y.I. Zozulya, M. Alhabeeb, B. Anasori, K. Malesky, Y. Gogotsi. Synthesis and Optical Properties of 2D Carbide MXenes, Book of Abstracts for 11th International Scientific-Technical Conference "Composite Materials", National Technical University of Ukraine "Igor Sikorsky Kyiv Polytechnic Institute", April 2018, рр.118-120. UDC 542;546;62.
Acknowledgement. This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Skłodowska-Curie grant agreement No 777810.

2018 IEEE 8th International Conference on Nanomaterials: Applications & Properties
To contact MXene supplier Carbon-Ukraine company (Y-Carbon ltd) or to get a quota with a price on MXene or MAX phase
2018 IEEE 8th International Conference on Nanomaterials: Applications & Properties, September 09-14, 2018 |
|
|




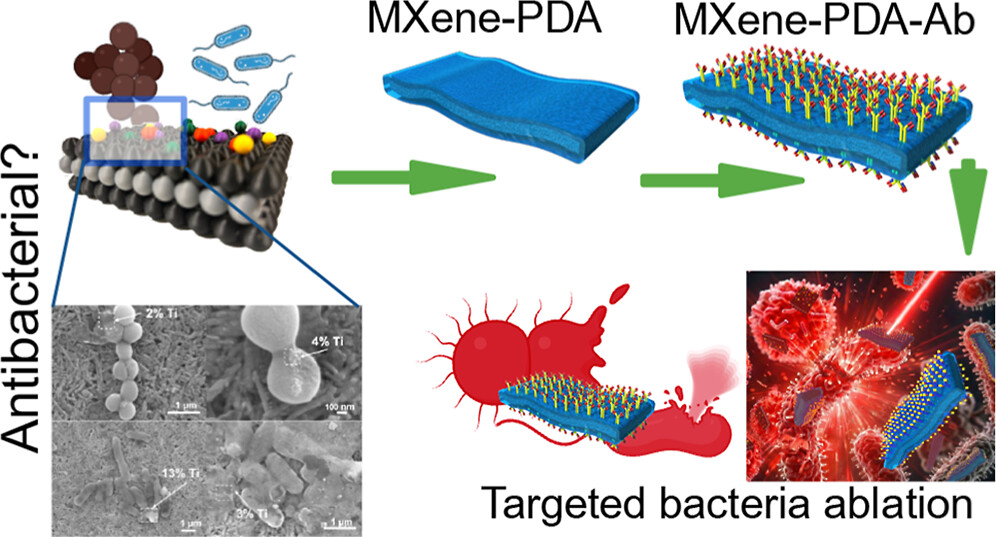 Do MXene nanosheets possess intrinsic antibacterial activity? A systematic study of high-quality Ti-, V-, and Nb-based MXenes reveals negligible inherent antimicrobial effects while highlighting their strong potential for targeted photothermal antibacterial therapy.
Do MXene nanosheets possess intrinsic antibacterial activity? A systematic study of high-quality Ti-, V-, and Nb-based MXenes reveals negligible inherent antimicrobial effects while highlighting their strong potential for targeted photothermal antibacterial therapy. Highlights
Highlights We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development.
We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development. Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments.
Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments. Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
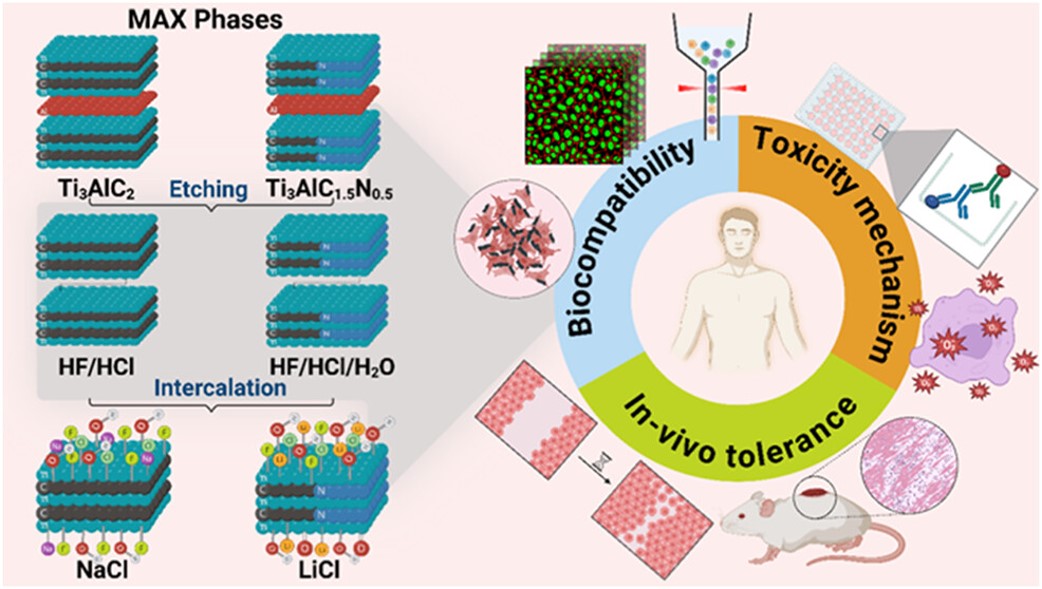 MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.
MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.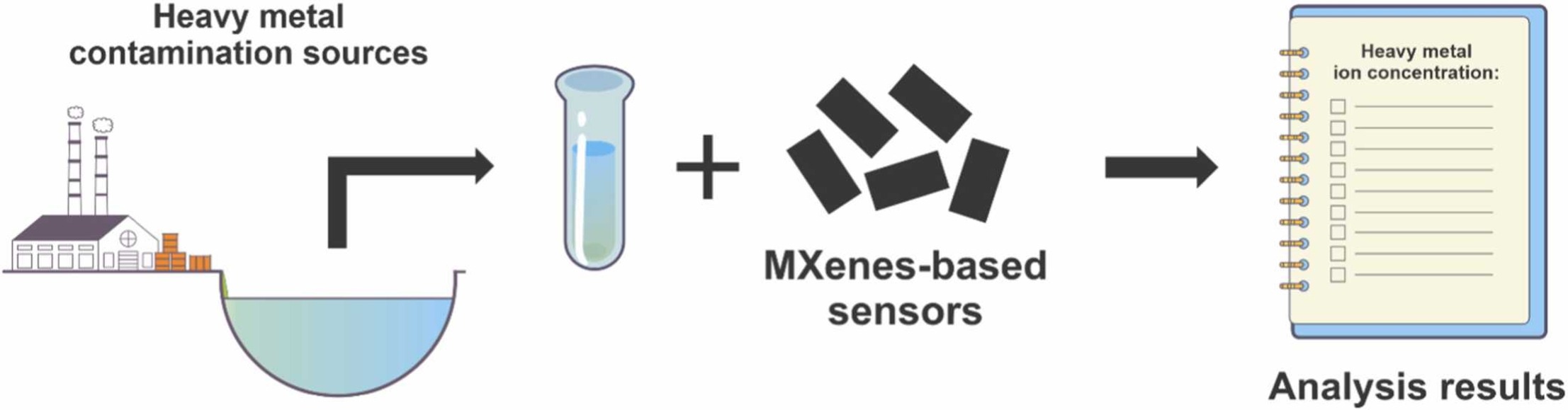 An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
 Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme.
Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme. Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved!
Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved! Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!
Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!  Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!
Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!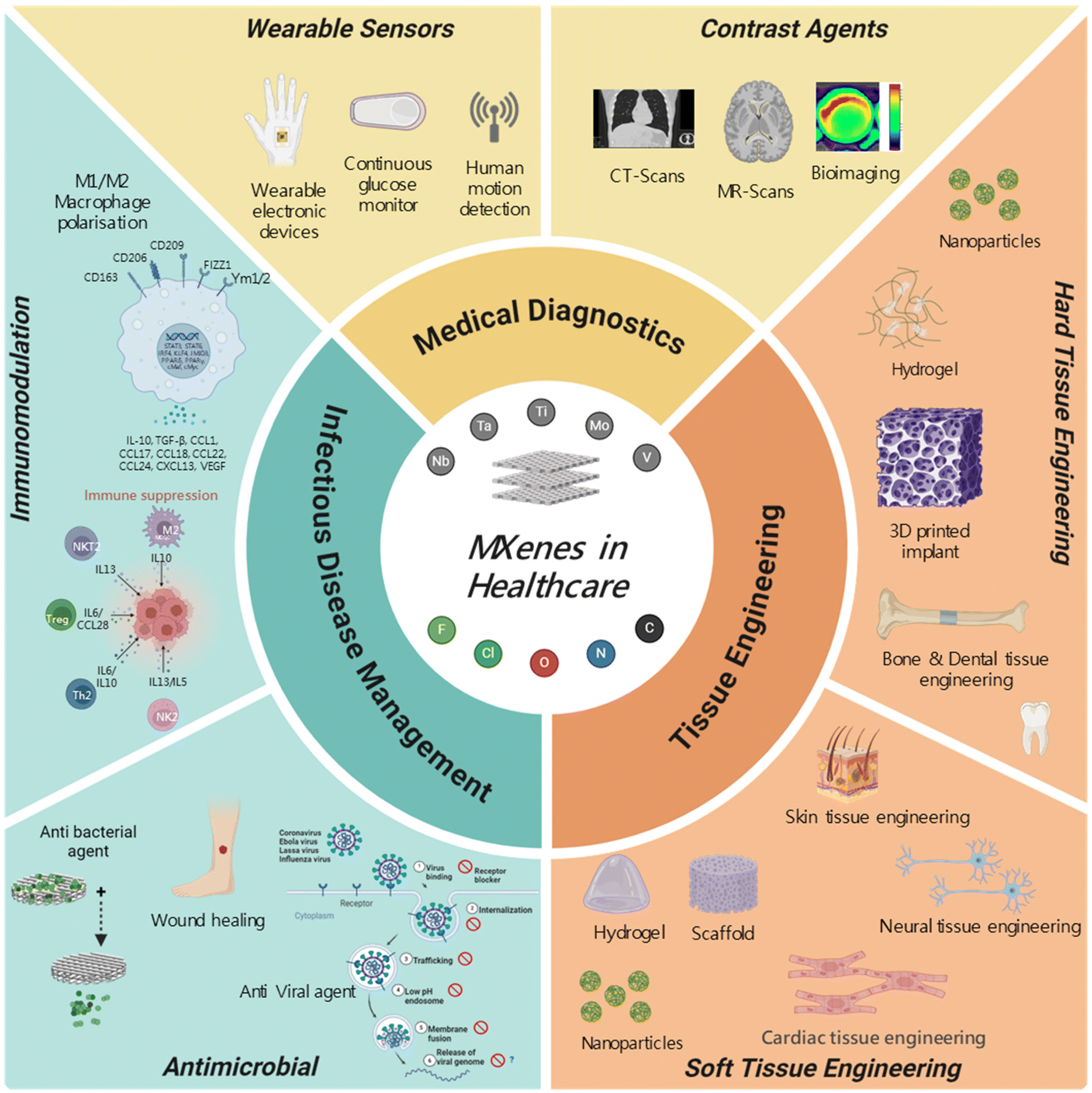 We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.
We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.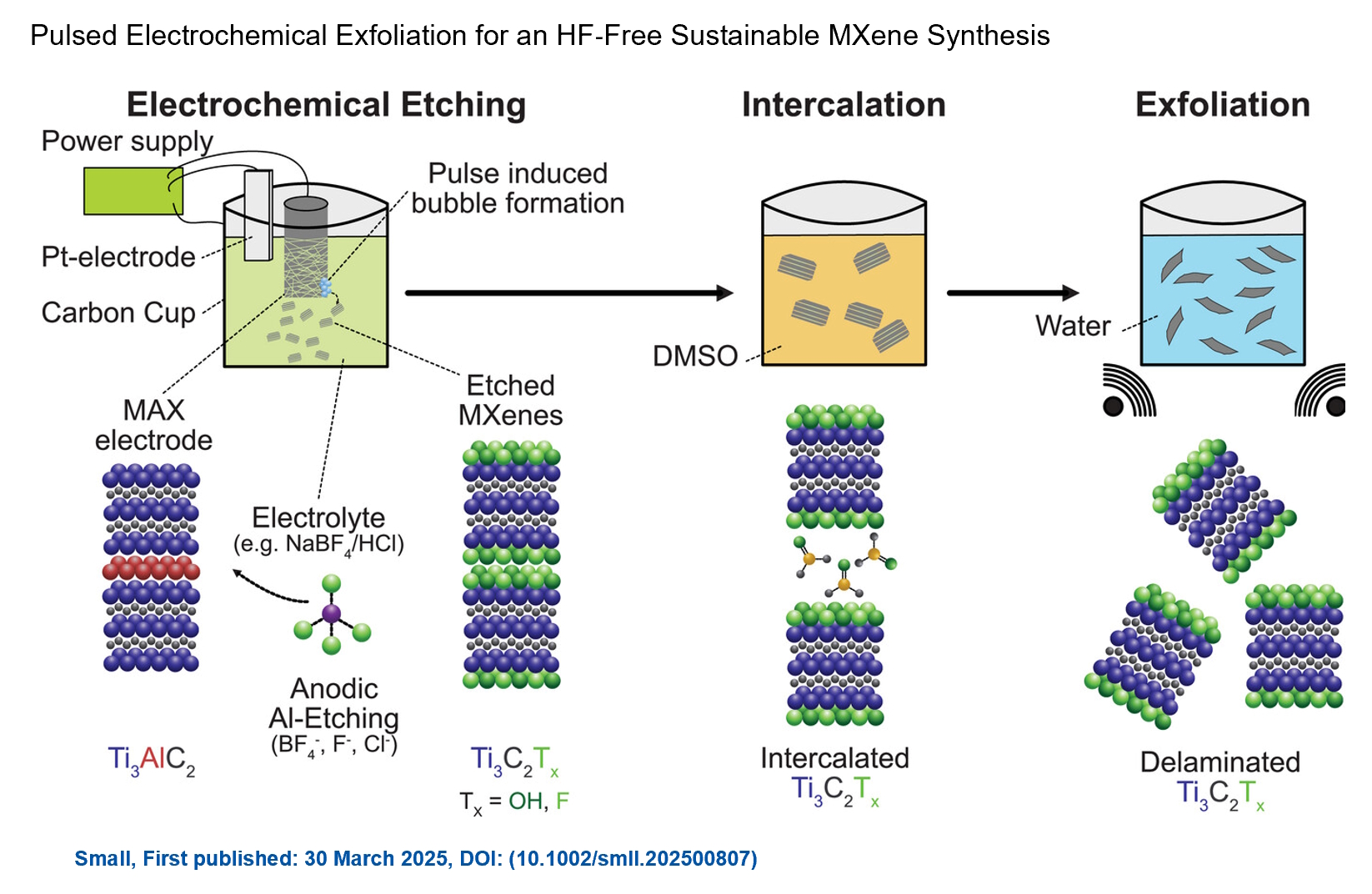 Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.
Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.