 CIMTEC 2014 - 13th International Conference on Modern Materials and Technologies -was held in Montecatini Terme, Tuscany, Italy, June 8 to 19, 2014.
CIMTEC 2014 - 13th International Conference on Modern Materials and Technologies -was held in Montecatini Terme, Tuscany, Italy, June 8 to 19, 2014.
CIMTEC 2014 consisted of the 13th International Ceramics Congress (June 8-13) and of the 6th Forum on New Materials (June 15-19), each of them including a number of Symposia, Special Sessions, and Conferences.
As a major long standing event for the international materials community, CIMTEC again gathered together a large and qualified audience of materials scientists, physicists, chemists and engineers as well as of experts of a wide range of the most demanding application areas of modern materials, from the molecular and nanoscales to large complex integrated systems.
Nanomaterials Group from Drexel Nanomaterials Institute of Drexel University, USA, lead by professor Yury Gogotsi visited International Conference on Modern Materials and Technologies CIMTEC 2014 in Montecatini Terme, to take part in the 13th International Ceramics Congress and the 6th Forum on New Materials.
13th International Ceramics Congress, June 8-13 2014
SYMPOSIUM CG
PROGRESS IN NANO-LAMINATED TERNARY CARBIDES AND NITRIDES (MAX PHASES) AND DERIVATIVES THERE OF (MXENES)
CG:HP02 Optical and Electronic Properties of Two-dimensional Ti3C2 Epitaxial Thin Films (Hot Poster)
J. HALIM1,2,3, M.R. Lukatskaya1,2, K.M. Cook1,2, Jun Lu3, C.R. Smith1,2,L.-A. Näslu nd3, S.J. May1, L. Hultman3, Y. Gogotsi1,2, P. Eklu nd3, M.W.Barsoum1, 1Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering, Drexel University,Philadelphia, PA, USA; 2A.J. Drexel Nanotechnology Institute, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, USA, Dept. of Materials Science & Engineering, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, USA; 3Thin Film Physics Division, Dept. of Physics, Chemistry and Biology (IFM), Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden
Abstract
Since the discovery of graphene, two-dimensional (2D) materials receive growing interest because of their unique properties as compared to their bulk counterparts. Although graphene has garnered the lion’s share of this attention, other 2D materials beyond MoS2 and BN are being sought out. Recently, a new family of 2D materials of early transition metal carbides and carbonitrides (Ti2C, Ti3C2, Ti3CN, V2C, Nb2C, Ta4C3 and more) known as MXenes has been discovered. Herein we show the fabrication of a 2D epitaxial Ti3C2 thin film, formed by the selective etching of Al from magnetron sputter-grown Ti3AlC2.
The optical transmittance, electrical resistivity, and magnetoresistance of the films were also measured. These data show that the films are up to ~ 90% transparent in the visible to infrared range, and that metallic-like conductive behavior is exhibited down to ~ 100 K. At temperatures below 100 K, resistivity of the films increased with decreasing temperature and magnetoresistance proved to be negative, due to a weak localization phenomenon characteristic of 2D films. These results illustrate the potential for the use of Ti3C2 thin films as transparent conductive electrodes, as well as in electrical, photonic and sensing applications.
CG-5:IL01 MXenes: 2D hosts for Ions in Electrochemical Energy Storage Systems M. Naguib, M. Lukatskaya, o. Mashtalir, Y. Gogotsi, M. Barsoum, Department of Materials science & engineering, and A.J. Drexel Nanotechnology Institute, Drexel University, Philadelphia, Pa, USA
Abstract
Recently we developed a new family of two-dimensional (2D) early transition metal carbides and carbonitrides, that we labeled MXenes. MXenes are produced by selective etching of the A-group layers from MAX phases. The latter is a large family of ternary layered metal carbides and/or nitrides. The etching process is carried out in an aqueous hydrofluoric acid. Thus, the as synthesized MXenes surface is terminated by O, OH and/or F. To date the following MXenes have been produced: Ti3C2, Ti2C, V2C, Nb2C, Ta4C3, TiNbC, (V0.5Cr0.5)3C2, and Ti3CN. Unlike conventional transition metal carbides, MXenes were found to be promising electrode materials in lithium-ions batteries (LIBs).
MXenes showed an excellent ability to handle cycling rates that are considerably faster than commercial graphite anodes can handle in LIBs (up to 40C). MXenes can also be used in electrochemical capacitors. At >300 F/cm3, the volumetric capacitance of MXenes was superior to that of activated carbon – the material of choice at this time. Herein we report on the latest progress in synthesis and use of MXenes as hosts for ions in electrochemical energy storage systems.
6th Forum on New Materials, June 15-19 2014
Symposium FC
Electrochemical Energy Storage Systems: the Next Evolution
FC-2:L05 Effect of Cation on Diffusion Coefficient of Ionic Liquids at Onion-like Carbon Electrodes
K. VAN AKEN1, J.K. MCDONOUGH1, SONG LI2, GUANG FENG2, S.M. CHATHOTH3, 5, E. MAMONTOV3, P.F. FULVIO4, P.T. CUMMINGS2, SHENG DAI4, Y. GOGOTSI1, 1Department of Materials Science and Engineering & A.J. Drexel Nanotechnology Institute, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA, USA; 2Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN, USA; 3Chemical and Engineering Materials Division, Neutron Sciences Directorate, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, USA; 4Chemical Science Division, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN, USA; 5Department of Physics and Materials Science, City University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
Abstract
While most supercapacitors are limited in their performance by the electrolyte stability, using neat ionic liquids (ILs) can expand the voltage window and temperature range of operation. Three different techniques were used to investigate the characteristics of three ILs in a comprehensive approach for a new field of electrolytes. Exohedral onion-like carbon (OLC) was chosen as the electrode material, allowing the behavior of ILs to be investigated without the influence of the carbon structure. In this study, ILs with bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide as anion were investigated as the electrolyte in OLC-based electrochemical capacitors.
To probe the effect of cations on the electrochemical performance of supercapacitors, three different cations were used: 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium, 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium, and 1,6-bis(3-methylimidazolium-1-yl). A series of electrochemical characterization tests were performed. Diffusion coefficients were measured using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and correlated with quasielastic neutron scattering and molecular dynamics simulation. The IL with the smaller sized cation had a larger diffusion coefficient, leading to higher capacitance at faster cycling rates. Electrolyte performance was also correlated with increasing temperature.
Source: www.cimtec-congress.org
Related Items:
12th International Ceramics Congress CIMTEC 2010, Montecatini Terme, Florence, Italy 6-18, June 2010





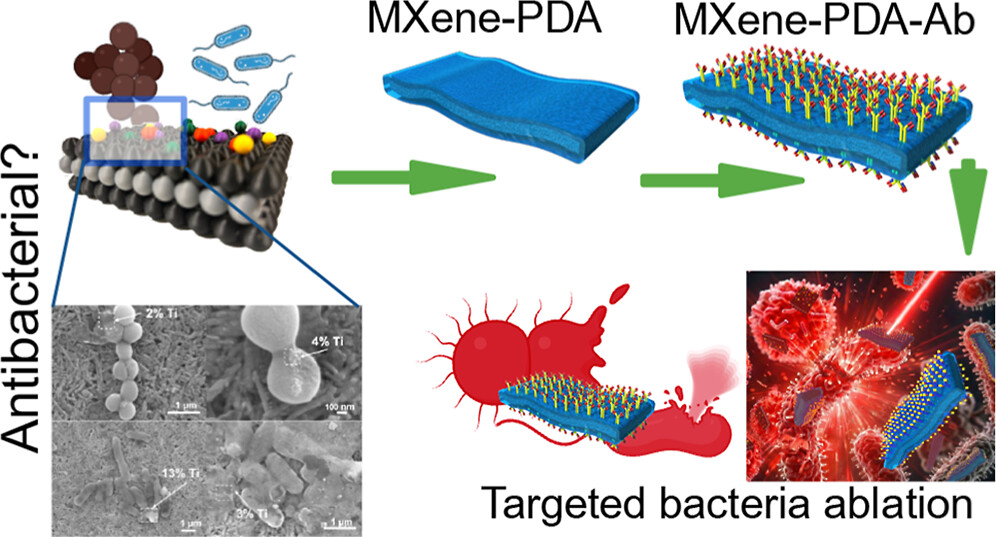 Do MXene nanosheets possess intrinsic antibacterial activity? A systematic study of high-quality Ti-, V-, and Nb-based MXenes reveals negligible inherent antimicrobial effects while highlighting their strong potential for targeted photothermal antibacterial therapy.
Do MXene nanosheets possess intrinsic antibacterial activity? A systematic study of high-quality Ti-, V-, and Nb-based MXenes reveals negligible inherent antimicrobial effects while highlighting their strong potential for targeted photothermal antibacterial therapy. Highlights
Highlights We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development.
We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development. Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments.
Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments. Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
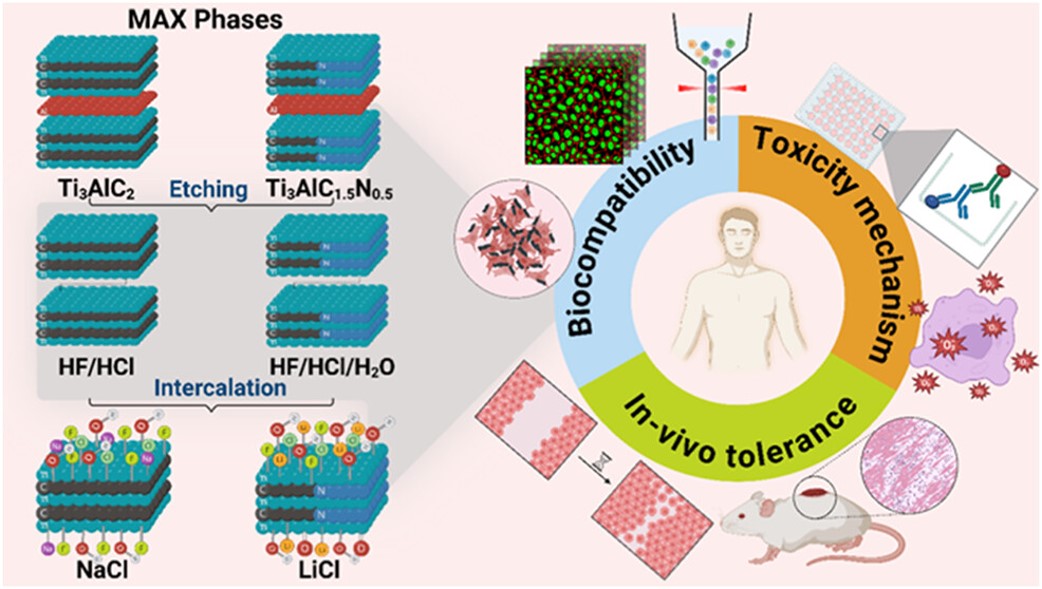 MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.
MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.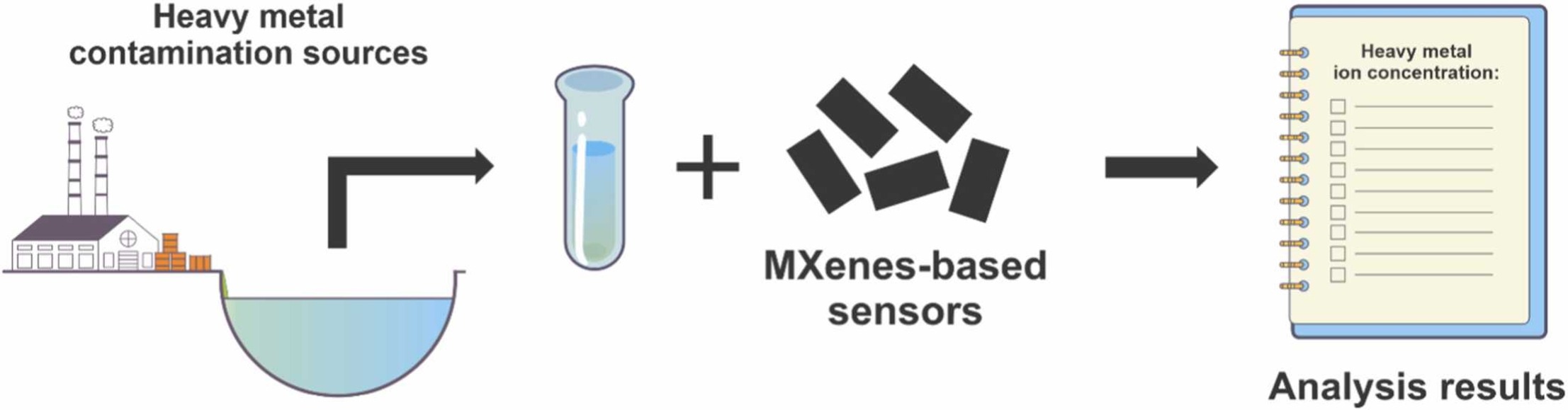 An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
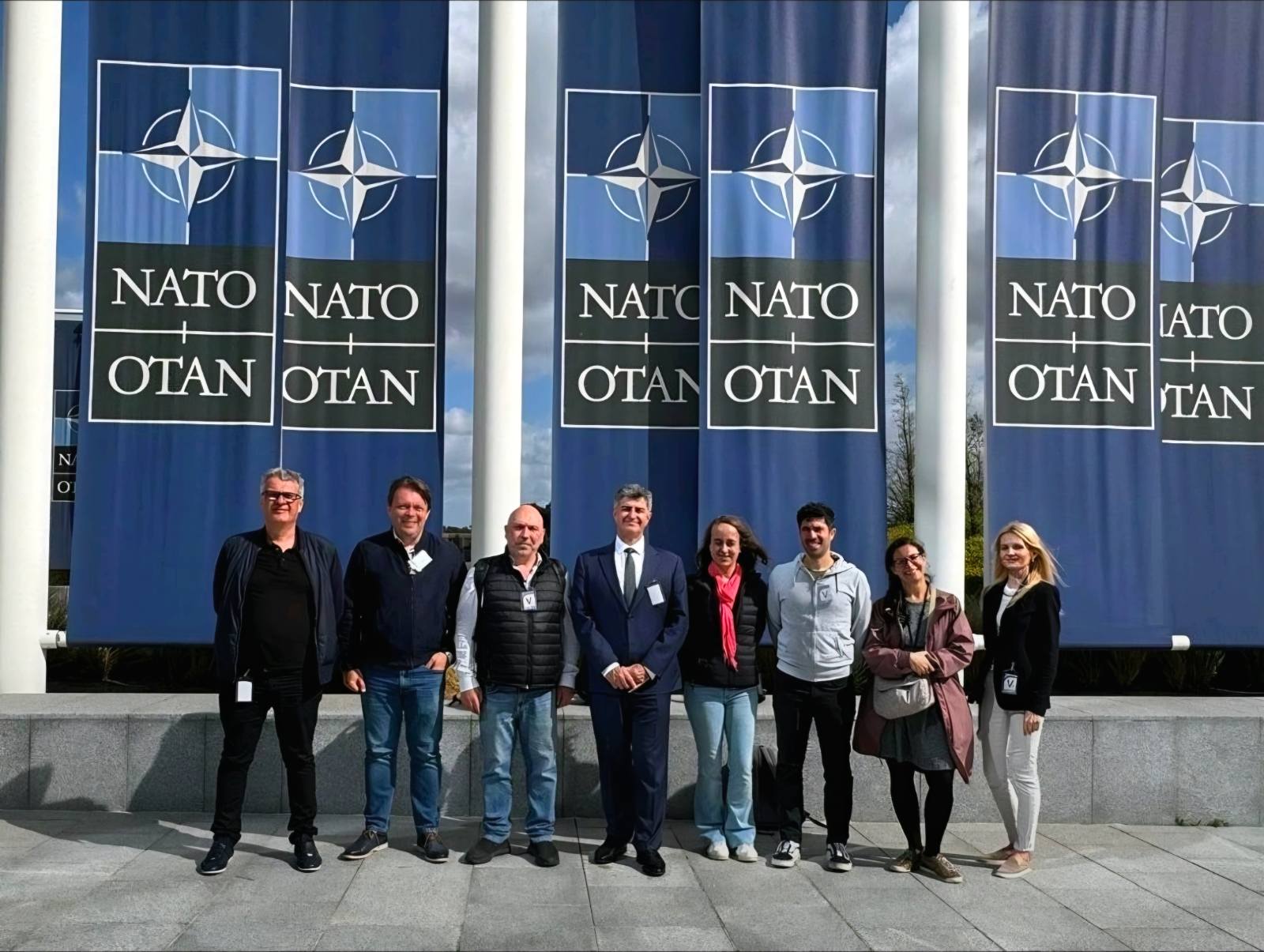 Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme.
Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme. Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved!
Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved! Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!
Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!  Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!
Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!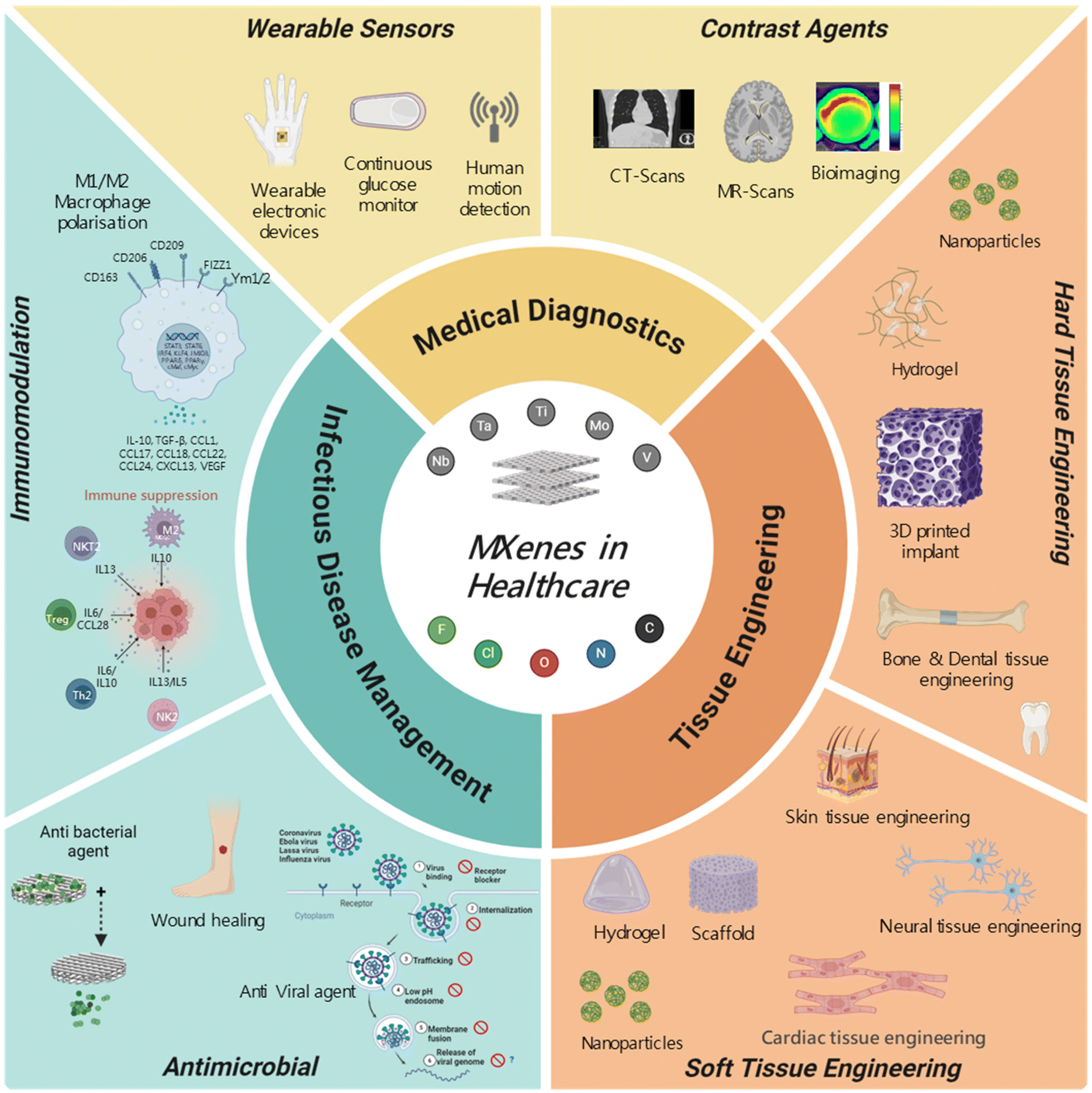 We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.
We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.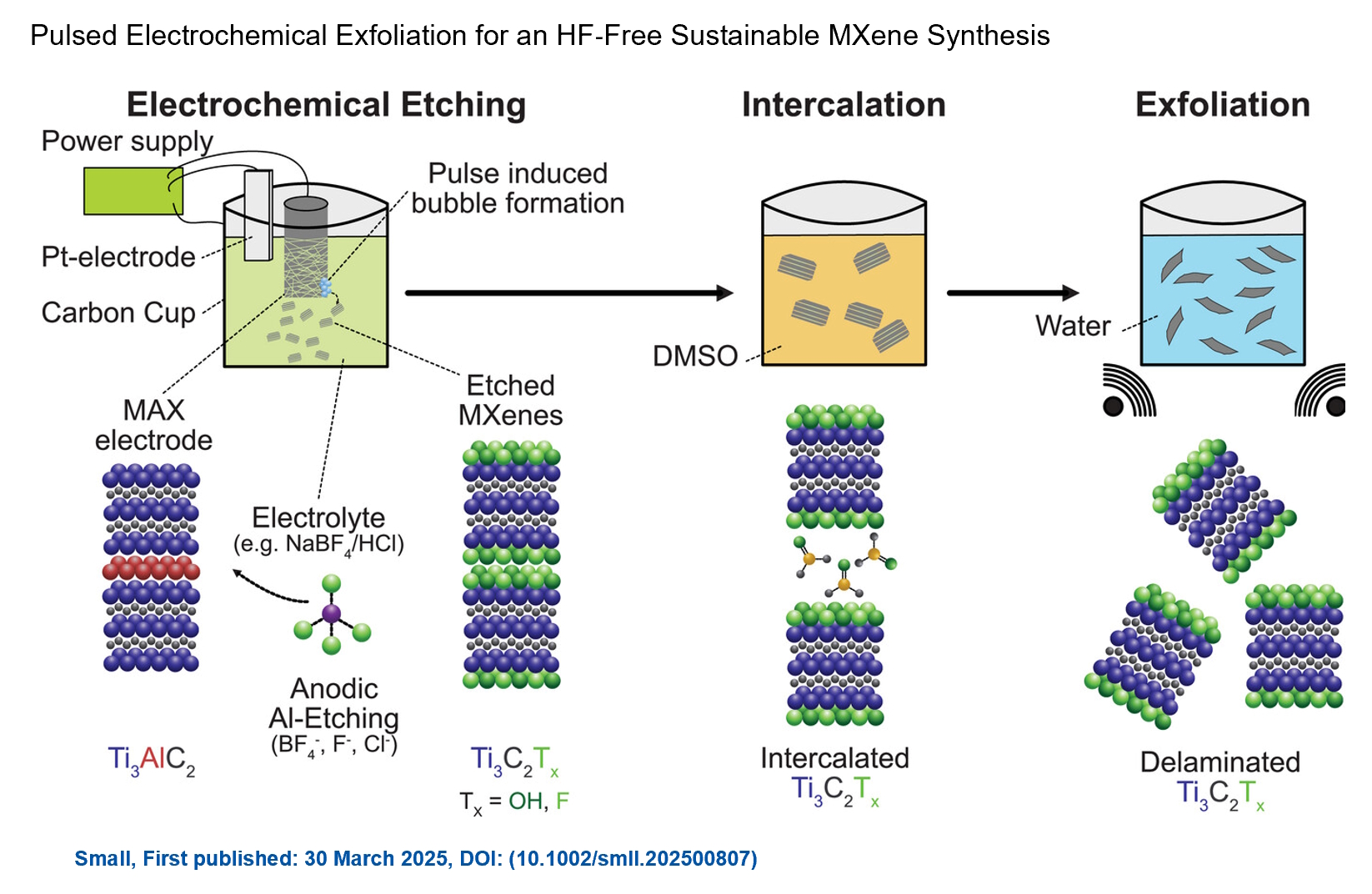 Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.
Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.