While lithium-ion batteries, widely used in mobile devices from cell phones to laptops, have one of the longest lifespans of commercial batteries today, they also have been behind a number of recent meltdowns and fires due to short-circuiting in mobile devices. In hopes of preventing more of these hazardous malfunctions researchers at Drexel University have developed a recipe that can turn electrolyte solution — a key component of most batteries — into a safeguard against the chemical process that leads to battery-related disasters.
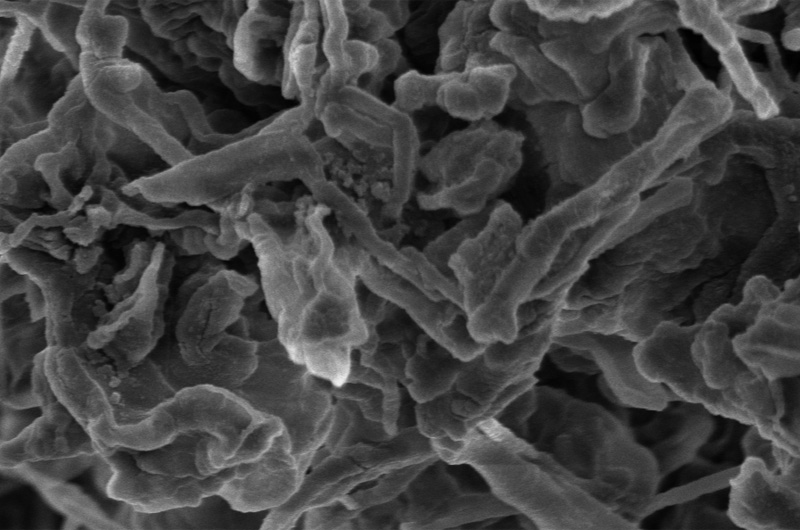

As batteries are used and charged, the electrochemical reaction results in the movement of ions between the two electrodes of a battery, which is the essence of an electrical current. Over time, this repositioning of ions can create tendril-like buildups — almost like stalactites forming inside a cave. These battery buildups, called dendrites, are one of the main causes of lithium battery malfunction. As dendrites form inside the battery over time, they can reach the point where they push through the separator, a porous polymer film that prevents the positively charged part of a battery from touching the negatively charged part. When the separator is breached, a short-circuit can occur, which can also lead to a fire since the electrolyte solution in most lithium-ion batteries is highly flammable.
To avoid dendrite formation and minimize the probability of fire, current battery designs include one electrode made of graphite filled with lithium instead of pure lithium. The use of graphite as the host for lithium prevents the formation of dendrites. But lithium intercalated graphite also stores about 10 times less energy than pure lithium. The breakthrough made by Gogotsi’s team means that a great increase in energy storage is possible because dendrite formation can be eliminated in pure lithium electrodes.
“Battery safety is a key issue for this research,” Gogotsi said. “Small primary batteries in watches use lithium anodes, but they are only discharged once. When you start charging them again and again, dendrites start growing. There may be several safe cycles, but sooner or later a short-circuit will happen. We want to eliminate or, at least, minimize that possibility.”
Gogotsi and his collaborators from Tsinghua University in Beijing, and Hauzhong University of Science and Technology in Wuhan, China, focused their work on making lithium anodes more stable and lithium plating more uniform so that dendrites won’t grow.
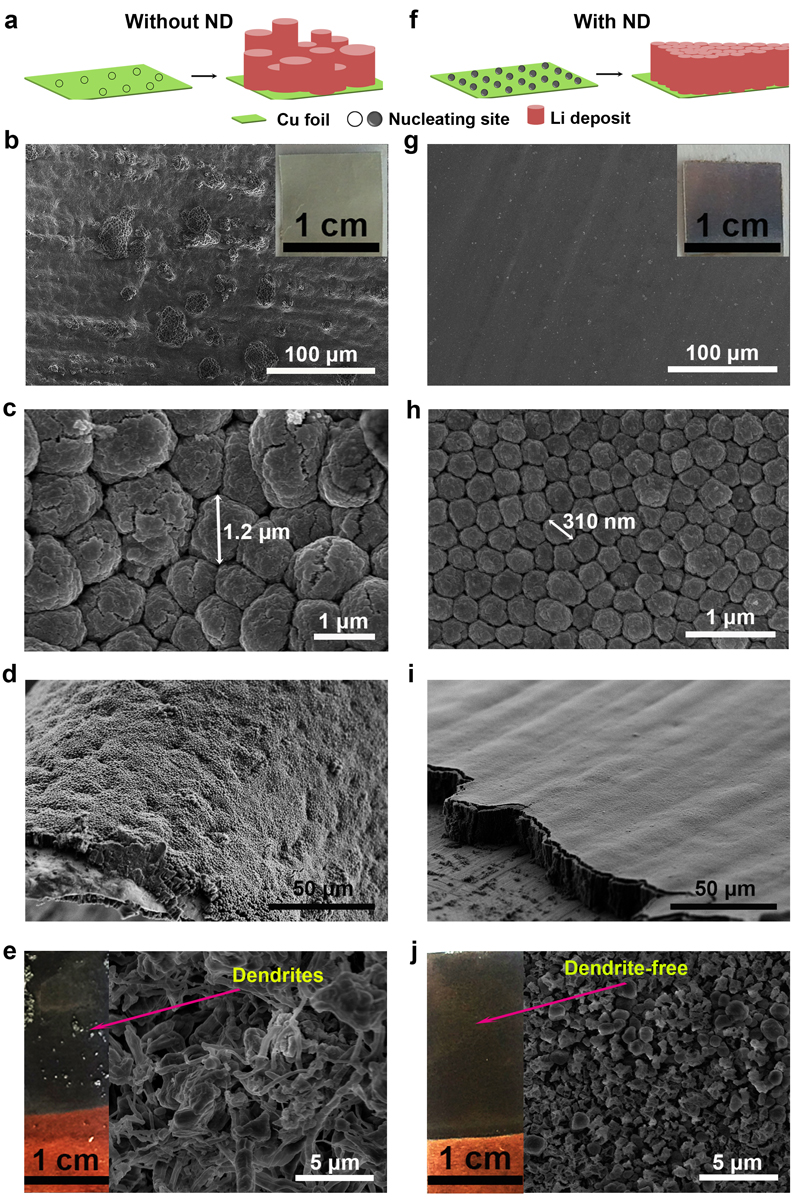

The researchers found this property to be exceedingly useful for eliminating dendrite formation. In the paper, they explain that lithium ions can easily attach to nanodiamonds, so when they are plating the electrode they do so in the same orderly manner as the nanodiamond particles to which they’re linked. They report in the paper that mixing nanodiamonds into the electrolyte solution of a lithium ion battery slows dendrite formation to nil through 100 charge-discharge cycles.
If you think about it like a game of Tetris, that pile of mismatched blocks inching perilously close to “game over” is the equivalent of a dendrite. Adding nanodiamonds to the mix is kind of like using a cheat code that slides each new block into the proper place to complete a line and prevent a menacing tower from forming.
Gogotsi notes that his group’s discovery is just the beginning of a process that could eventually see electrolyte additives, like nanodiamonds, widely used to produce safe lithium batteries with a high energy density. Initial results already show stable charge-discharge cycling for as long as 200 hours, which is long enough for use in some industrial or military applications, but not nearly adequate for batteries used in laptops or cell phones. Researchers also need to test a large number of battery cells over a long enough period of time under various physical conditions and temperatures to ensure that dendrites will never grow.
“It’s potentially game-changing, but it is difficult to be 100 percent certain that dendrites will never grow,” Gogotsi said. “We anticipate the first use of our proposed technology will be in less critical applications — not in cell phones or car batteries. To ensure safety, additives to electrolytes, such as nanodiamonds, need to be combined with other precautions, such as using non-flammable electrolytes, safer electrode materials and stronger separators.”
Source: http://drexel.edu/now/archive/2017/August/Nanodiamonds-make-batteries-safer/



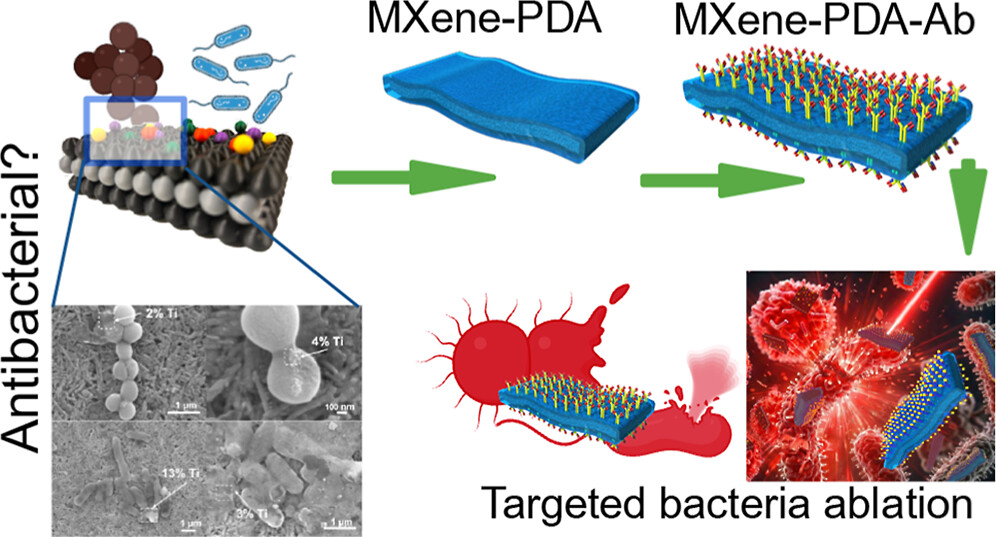 Do MXene nanosheets possess intrinsic antibacterial activity? A systematic study of high-quality Ti-, V-, and Nb-based MXenes reveals negligible inherent antimicrobial effects while highlighting their strong potential for targeted photothermal antibacterial therapy.
Do MXene nanosheets possess intrinsic antibacterial activity? A systematic study of high-quality Ti-, V-, and Nb-based MXenes reveals negligible inherent antimicrobial effects while highlighting their strong potential for targeted photothermal antibacterial therapy. Highlights
Highlights We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development.
We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development. Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments.
Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments. Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
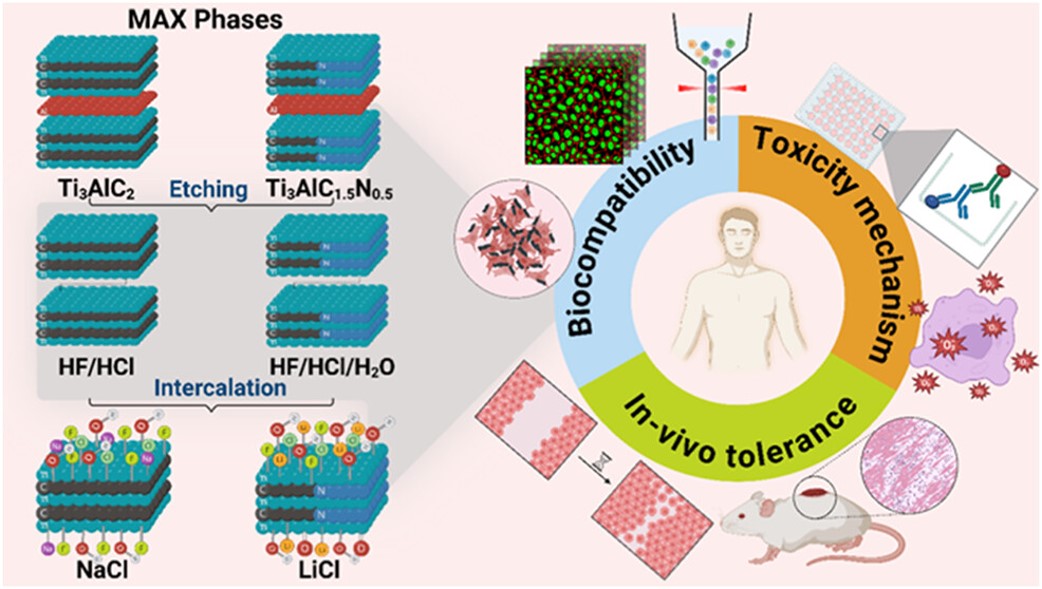 MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.
MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications. An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
 Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme.
Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme. Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved!
Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved! Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!
Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!  Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!
Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!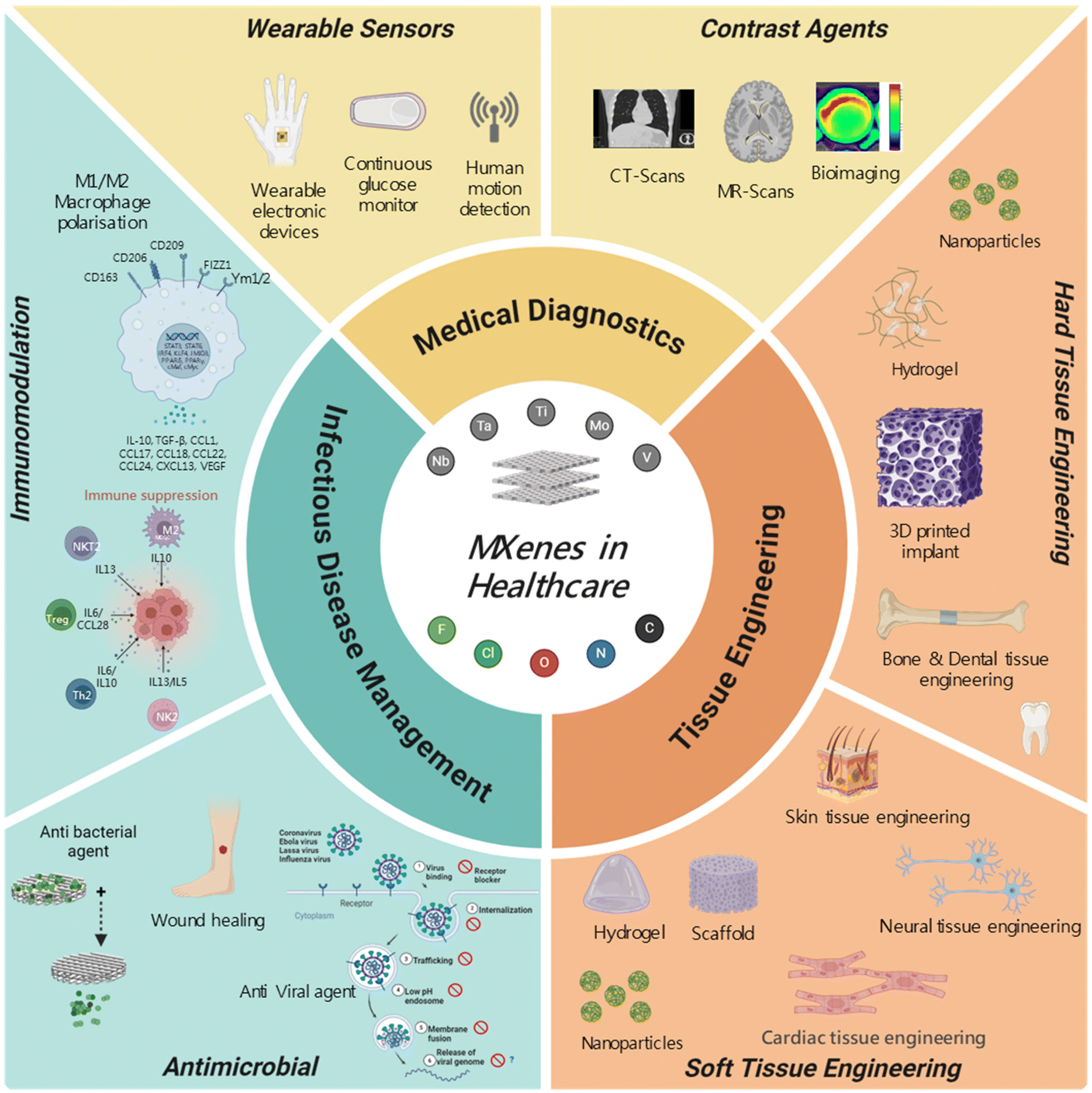 We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.
We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.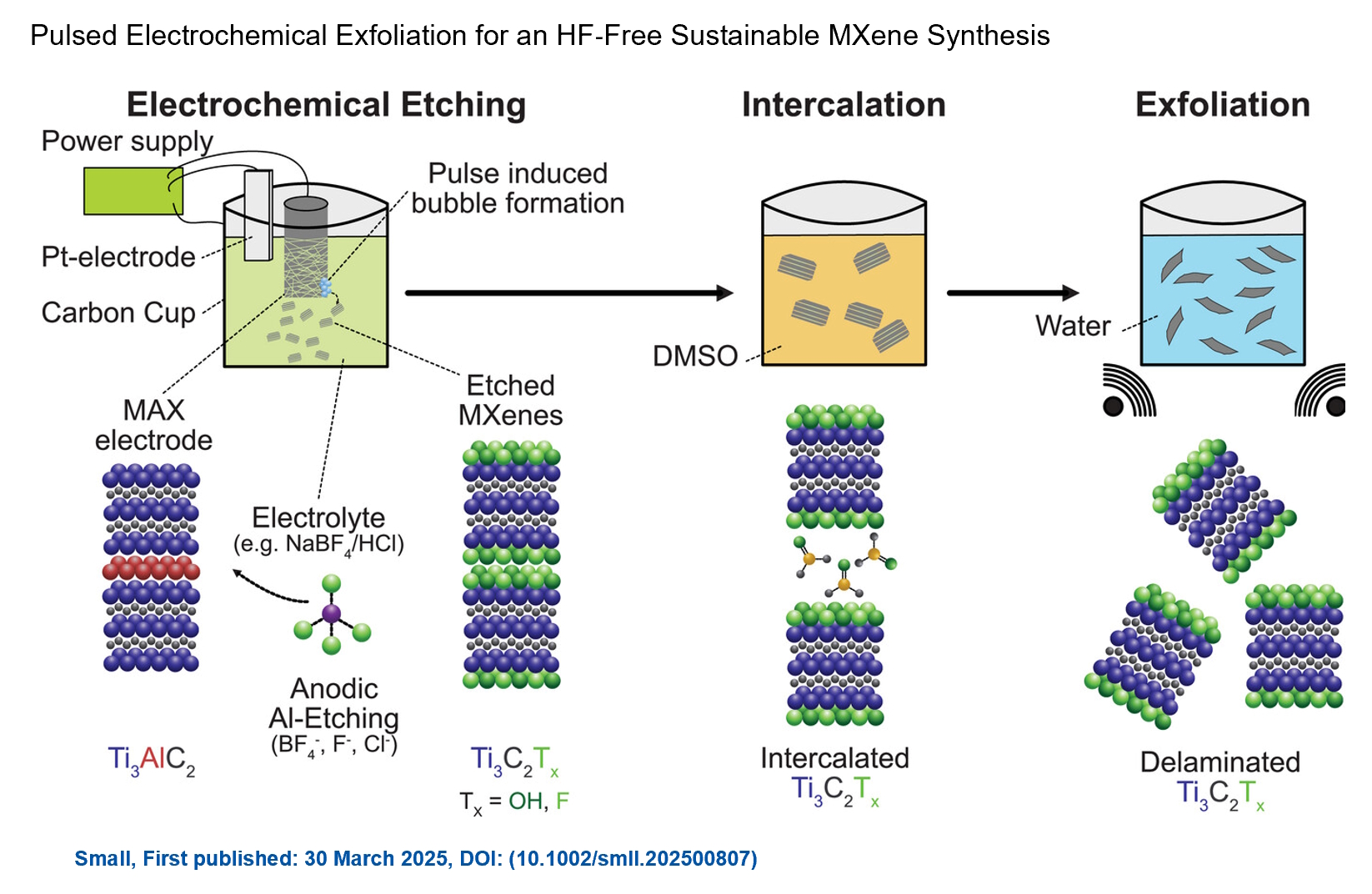 Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.
Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.