4th International Conference Nanobiophysics: Fundamental and Applied Aspects, 1-4 October 2015, Kyiv, Ukraine
Nanostructured tunable mesoporous carbon for energy and biomedical applications
O. Gogotsi1, B. Dyatkin2, Y. Gogotsi2, P. Simon³, Y. Zozulya1, B. Malinovskiy1, V. Zahorodna1
1 Materials Research Centre, 3, Akademika Krzhyzhanovskoho St, Kyiv 03680, Ukraine, E-mail: E-mail: Этот e-mail адрес защищен от спам-ботов, для его просмотра у Вас должен быть включен Javascript
2A. J. Drexel Nanomaterials Institute, and Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Drexel University, Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA, E-mail: Этот e-mail адрес защищен от спам-ботов, для его просмотра у Вас должен быть включен Javascript
³ Université Paul Sabatier-Toulouse III, CIRIMAT UMR-CNRS 5085, and RS2E, FR CNRS 3459, 118 Route de Narbonne, 31062 Toulouse, France. E-mail: Этот e-mail адрес защищен от спам-ботов, для его просмотра у Вас должен быть включен Javascript
Abstract
 We will discuss synthesis of carbide-derived carbon (CDC), which is a nanoporous carbon formed by selectively etching metal atoms from metal carbides [1]. CDCs are generally produced by chlorination of carbides in the 200–1200°C temperature range. Metals and metalloids are removed as chlorides, leaving behind a noncrystalline carbon with up to 80% open pore volume. A wide range of carbide precursors (TiC, SiC, B4C, VC, Mo2C, NbC as well as ternary carbides – Ti3AlC2, Ti2AlC, also known as MAX-phases) leads to a wide range of carbons with tailored porosity. The total volume and characteristic dimensions of meso- and nanopores can be predicted and achieved by selection of a binary or ternary carbide and variation of the chlorination process parameters. Due to a wide range of pore sizes (0.3–30 nm) and specific surface areas (300–2300 m2/g) of CDCs, a great potential for applications requiring large volumes of either micropores (
We will discuss synthesis of carbide-derived carbon (CDC), which is a nanoporous carbon formed by selectively etching metal atoms from metal carbides [1]. CDCs are generally produced by chlorination of carbides in the 200–1200°C temperature range. Metals and metalloids are removed as chlorides, leaving behind a noncrystalline carbon with up to 80% open pore volume. A wide range of carbide precursors (TiC, SiC, B4C, VC, Mo2C, NbC as well as ternary carbides – Ti3AlC2, Ti2AlC, also known as MAX-phases) leads to a wide range of carbons with tailored porosity. The total volume and characteristic dimensions of meso- and nanopores can be predicted and achieved by selection of a binary or ternary carbide and variation of the chlorination process parameters. Due to a wide range of pore sizes (0.3–30 nm) and specific surface areas (300–2300 m2/g) of CDCs, a great potential for applications requiring large volumes of either micropores (
The highly tunable porosity of CDC [1,2] has inspired fundamental studies of the effects of pore size, pore volume, and surface area on transport and adsorption of gases, ions and biomolecules. The unique properties of CDC allowed to use it in many demanding applications including H2 and methane storage, gas sorption, adsorbents, electrodes in batteries and supercapacitors [3], flow capacitors, molecular sieves, catalyst supports, water/air filters and medical devices, protein adsorption, tribology, extracorporeal devices for blood cleansing [4]. Such properties of CDC as good electrical conductivity combined with high surface area, large micropore volume, and pore size control allow its application as active material in electrodes for flow desalination [5], supercapacitors [6] as porous electrodes for capacitive deionization [7].
Chlorination of layered ternary MAX-phase carbides has made it possible to synthesize mesoporous carbons with large volumes of slit-shaped mesopores that can be used for purification of bio-fluids due to their excellent biocompatibility and ability to adsorb a range of inflammatory cytokines within the shortest time, which is crucial in sepsis treatment. The synthesized carbons, having tunable pore size with a large volume of slit-shaped mesopores, outperformed other materials in terms of efficiency of TNF-α removal. Cytokine removal from blood may help to bring under control the unregulated pro- and anti-inflammatory processes driving sepsis. Adsorption can remove toxins without introducing other substances into the blood. Therefore, hemoadsorption might have advantages over hemofiltration, having the same or better efficiency in the treatment of inflammatory diseases, being of lower cost and offering considerably better comfort for patients during and after the treatments [8].
Large mesopores in CDC from MAX phases are capable to accommodate most of the proteins due to their controlled porosity can be used for separation of different proteins molecules.
References:
[1] G. Yushin, Y. Gogotsi, A. Nikitin, Carbide Derived Carbon, in: Y.Gogotsi (Ed.), Nanomaterials Handbook, CRC Press, New York, 2006, pp. 237–280.
[2] Y. Gogotsi, A. Nikitin, H. Ye, W. Zhou, J.E. Fischer, B. Yi, H.C. Foley, M.W. Barsoum, Nature Materials 2 (2003) 591–594.
[3]. J. Chmiola, G. Yushin, Y. Gogotsi, C. Portet, P. Simon, P.L.Taberna, Anomalous Increase in Carbon Capacitance at Pore Sizes Less Than 1 Nanometer, Science 313 (2006) 1760–1763.
[4]G. Yushin, E. Hoffman, M.W. Barsoum, Y. Gogotsi, C.A. Howell, S.R. Sandeman, G.J. Phillips, A.W. Lloyd, S.V Mikhalovsky,Mesoporous carbide-derived carbon with porosity tuned for efficient adsorption of cytokines, Biomaterials, 27 (2006) 5755–5762.
[5] P. Simon, P.-L. Taberna, B. Daffos, E. Iwama, T. Tzedakis, Y. Gogotsi, K. Hatzell, O. Gogotsi, Method and device to remove ions form an electrolytic media, such as water desalination, using suspension of divided materials in a flow capacitor. European Patent Application 13305761.2-1360, filed June 6, 2013
[6]B. Dyatkin, O. Gogotsi, Y. Zozuly, B. Malinovskiy, P. Simon, Y. Gogotsi. High Capacitance of Coarse-Grained Carbide-Derived Carbon Particles. Abstract Book of the 4th International Symposium on Enhanced Electrochemical Capacitors, June 8-12 2015, Montpelier, France, p.143.
[7] Hatzell, K. B., Iwama, E., Daffos, B., Taberna, P. L., Tzedakis, T., Gogotsi, A., Gogotsi, Y. High Electrosorption Capacity Electrodes for Capacitive Deionization, 224th ECS Meeting (October 27–November 1, 2013), Meeting Abstracts (No. 4, pp. 235-235).
[8]. Mikhalovsky SV. Emerging technologies in extracorporeal treatment: Focus on adsorption. Perfusion-UK 2003;16(2):47–54.
Here you can find Book of Abstract of the Conference NBP 2015






 Highlights
Highlights We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development.
We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development. Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments.
Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments. Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
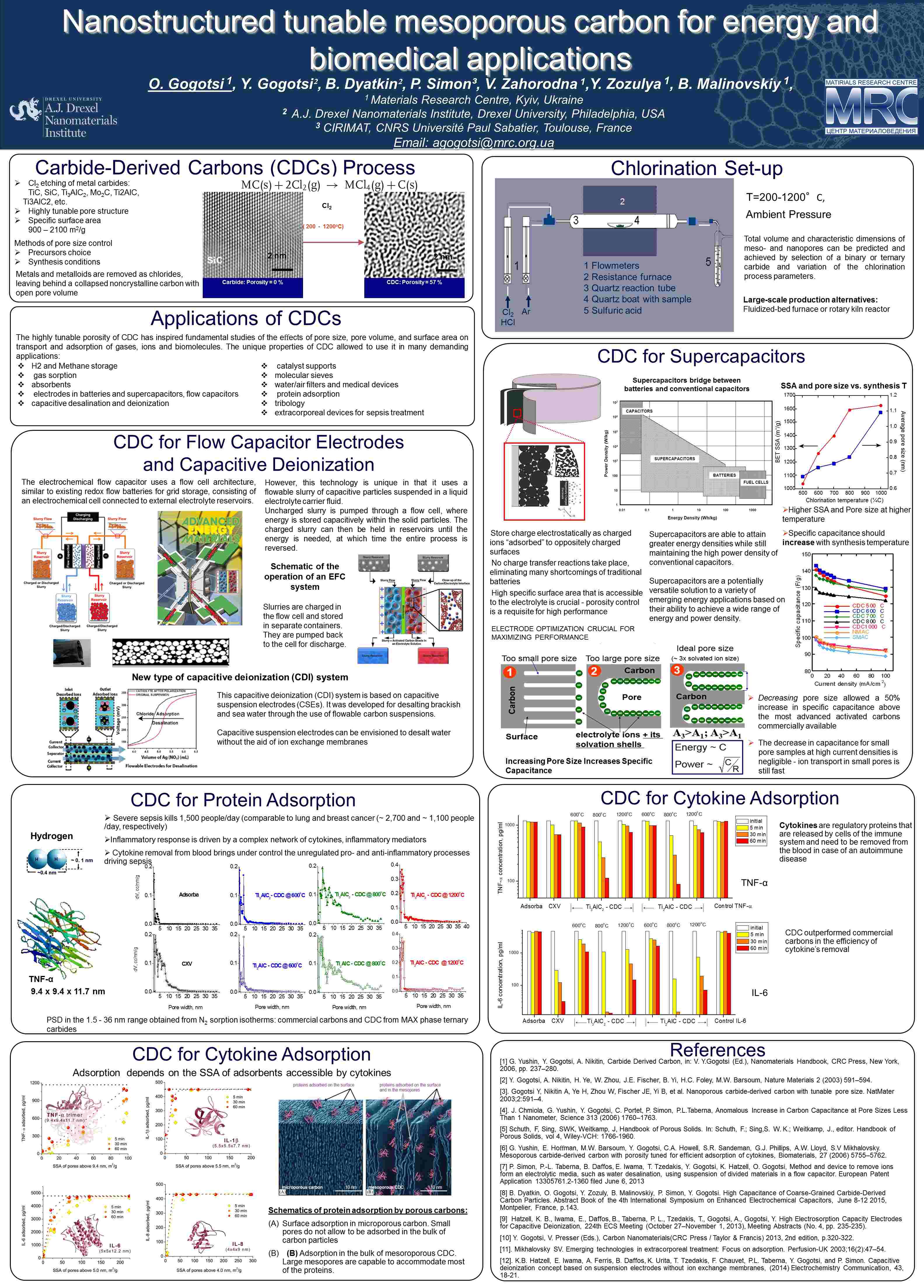
Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.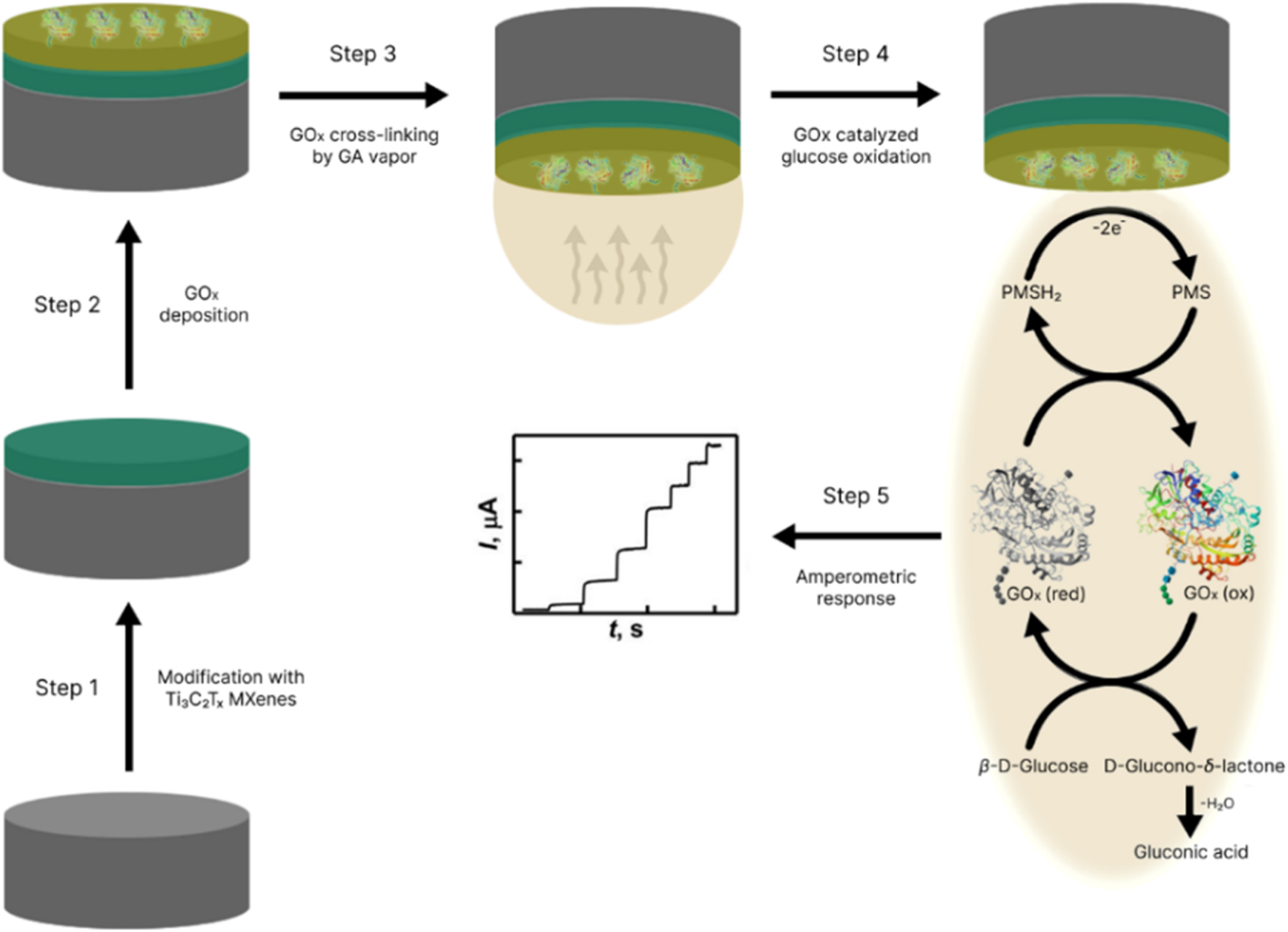
 MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.
MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications. An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
 Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme.
Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme. Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved!
Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved! Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!
Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!  Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!
Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!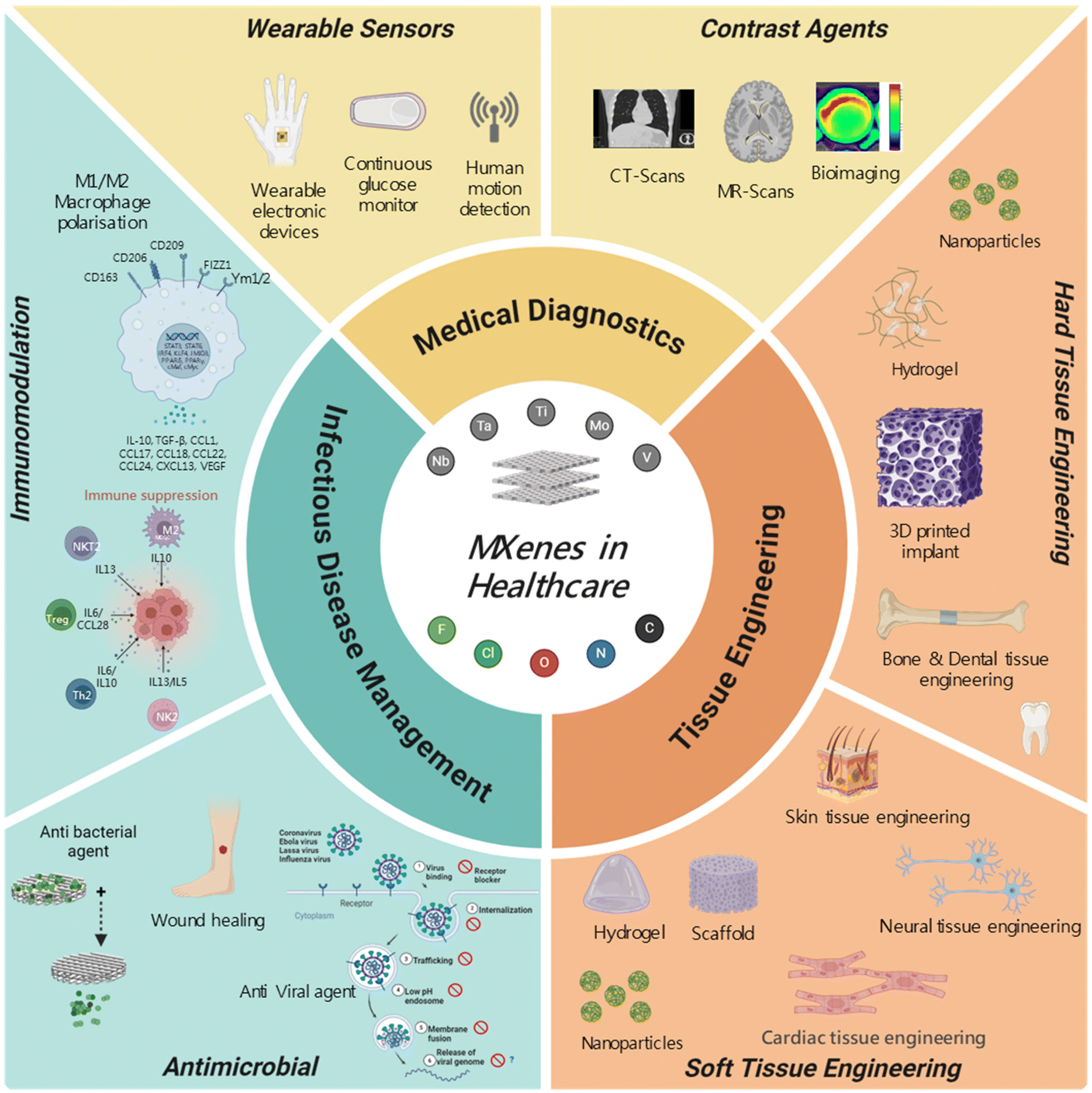 We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.
We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.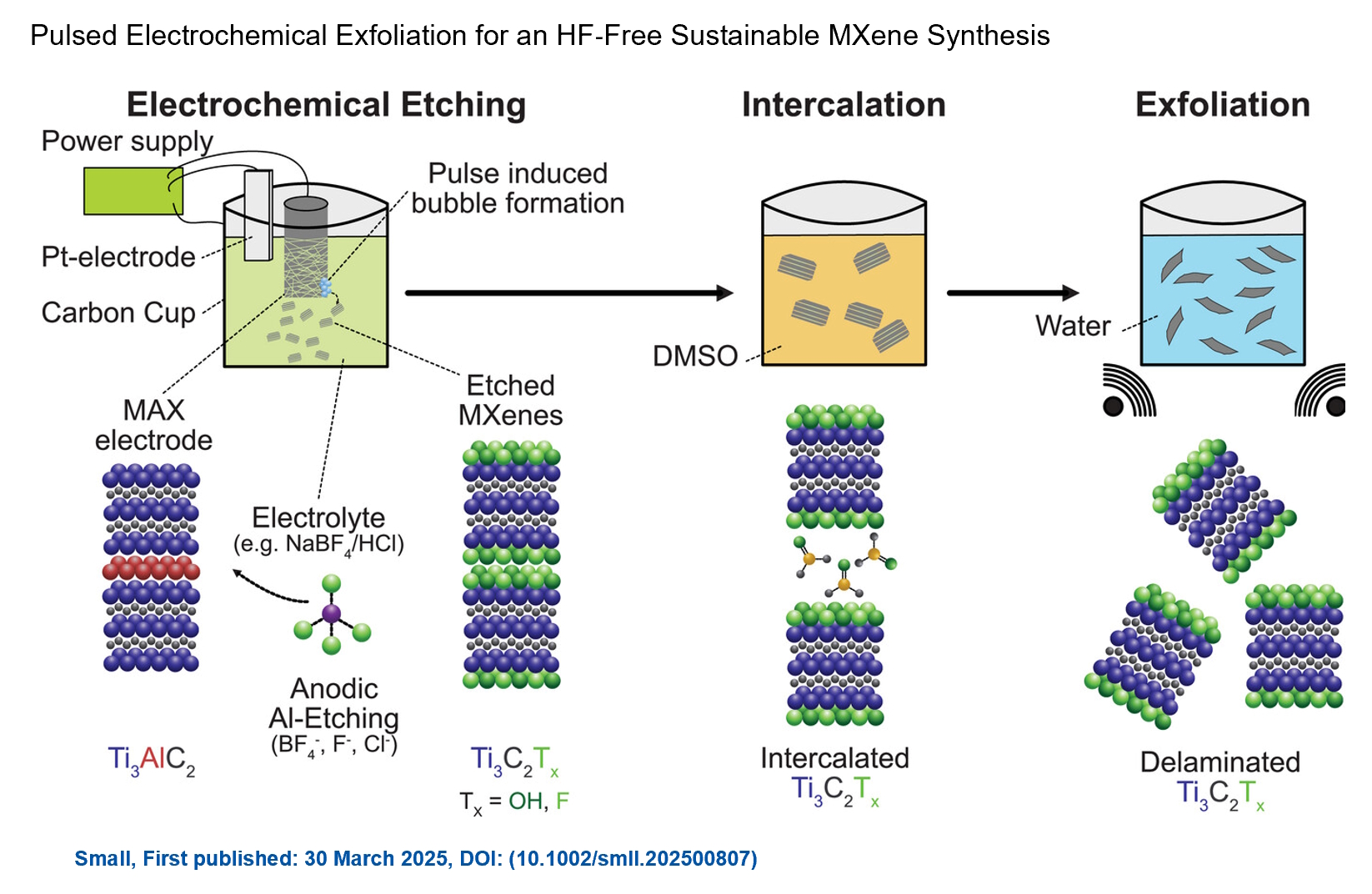 Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.
Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved. Congratulations to all collaborators with this interesting joint work!
Congratulations to all collaborators with this interesting joint work!