Symposium on Two-dimensional Nanomaterials 2015
10-11 March 2015, Melbourne, Australia

Two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterials, are emerging new class of nanomaterials with many fascinating properties and applications. This two-day event provides an ideal networking opportunity for researchers to communicate on their latest research.
The areas of focus for this meeting will include (but are not limited to) both advances in fundamental physics, chemistry, materials science, biology and computer modelling of 2D materials, including graphene, BN, MoS2 and transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) nanosheets, but also their applications in functional materials. Applications in areas of energy, the environment, nanomedicine and sensing are welcomed.
Professor Yury Gogotsi, Drexel University (USA) will give a Keynote Lecture at the Symposium on Two-dimensional Nanomaterials in Melbourne - "Two-Dimensional Carbides and Nitrides (MXenes): Synthesis, Properties and Electrochemical Applications" on Tuesday, March 10, 2015. Also he will give an invited talk at a post-conference Workshop at the Institute for Frontier Materials, Deakin University, Geelong, on "Capacitive Energy Storage Systems Utilizing Carbon Nanomaterials”.
Two-Dimensional Carbides and Nitrides (MXenes): Synthesis, Properties and Electrochemical Applications
Yury Gogotsi*
Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and A. J. Drexel Nanomaterials Institute,
Drexel University,
Philadelphia, PA 19104, USA
Этот e-mail адрес защищен от спам-ботов, для его просмотра у Вас должен быть включен Javascript
Two-dimensional (2D) solids – the thinnest materials available to us – offer unique properties and a potential path to device miniaturization. The most famous example is graphene, which is an atomically thin layer of carbon atoms bonded together in-plane with sp2 bonds. Recently, an entirely new family of 2D solids – transition metal carbides (Ti2C, Ti3C2, Nb4C3, etc.) and carbonitrides – was discovered by Drexel University scientists.1,2 Selective etching of the A-group element from a MAX phase results in formation of 2D Mn+1Xn solids, labeled “MXene”. Eleven different carbides and carbonitrides have been reported to date.2-5 Structure and properties of numerous MXenes have been predicted by the density functional theory, showing that MXenes can be metallic or semiconducting (up to 2 eV band gap), depending on their surface termination. Their elastic constants along the basal plane are expected to be higher than that of the binary carbides. Oxygen or OH terminated MXenes, are hydrophilic, but electrically conductive. Hydrazine, urea and other polar organic molecules can intercalate MXenes leading to an increase of the c lattice parameter of MXenes.3 When dimethyl sulfoxide was intercalated into Ti3C2, followed by sonication in water, a stable colloidal solution of single- and few-layer flakes was produced. One of the many potential applications for 2D Ti3C2 is in electrical energy storage devices, such as batteries, Li-ion capacitors and supercapacitors.4,6 Cations ranging from Na+ to Mg2+ and Al3+ intercalate MXenes. Ti3C2 paper electrodes, produced by vacuum assisted filtration of an aqueous dispersion of delaminated Ti3C2, show a higher capacity than graphite anodes and also can be charged/discharged at significantly higher rates. They also demonstrate very high intercalation capacitance (up to 900 F/cm3) in aqueous electrolytes.
References
1 M. Naguib, et al, Advanced Materials, 23 (37), 4207-4331 (2011)
2 M. Naguib, et al, ACS Nano 6 (2), 1322–1331 (2012)
3 O. Mashtalir, et al, Nature Communication, 4, 1716 (2013)
4 M. R. Lukatskaya, et al, Science, 341, 1502-1505 (2103)
5 M. Naguib, et al, Advanced Materials, 26, 992-1005 (2014)
6 M. Ghidiu, et al, Nature, 516, 78–81 (2014)



Source: www.deakin.edu.au



 Highlights
Highlights We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development.
We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development. Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments.
Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments. Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.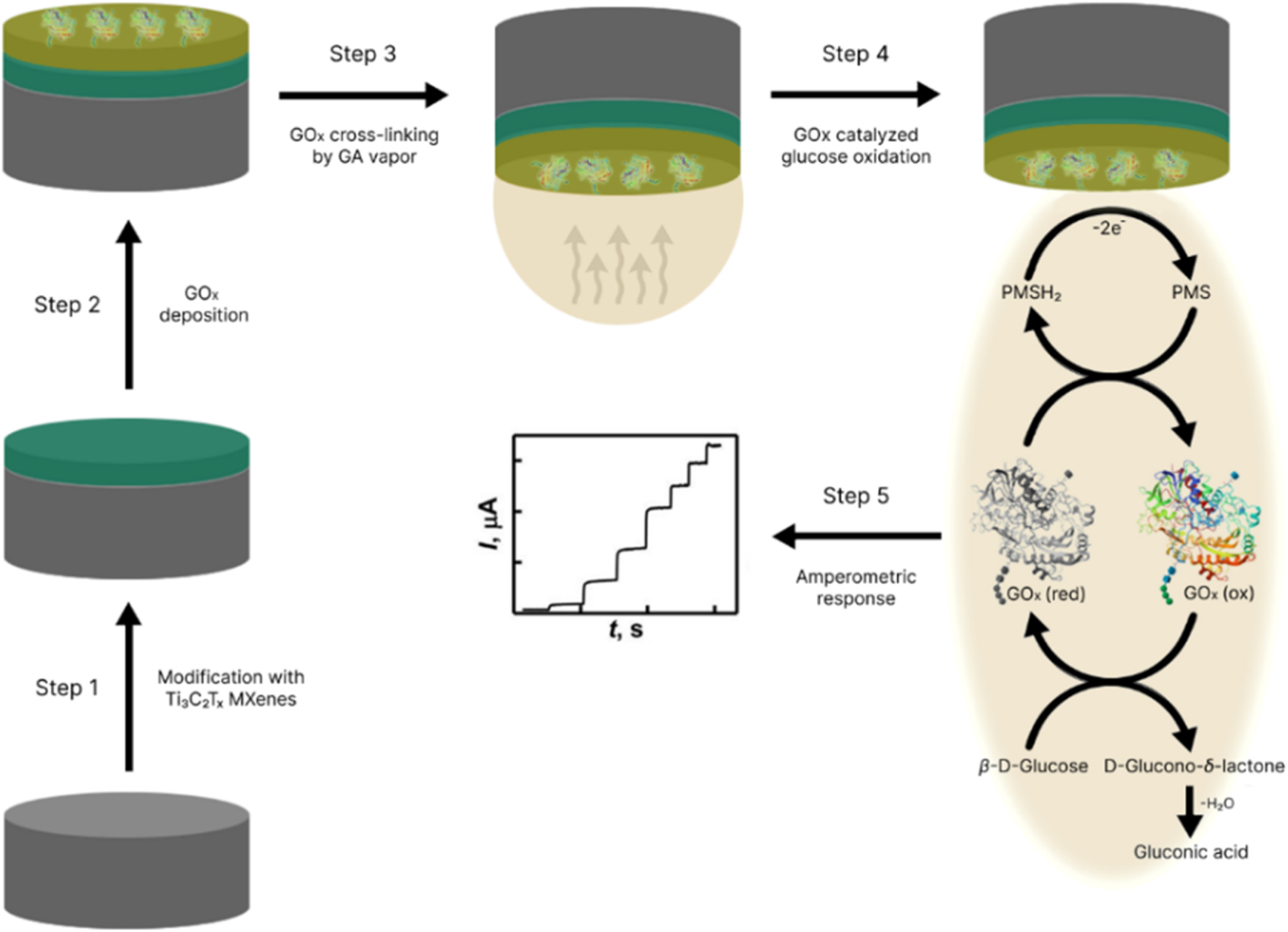
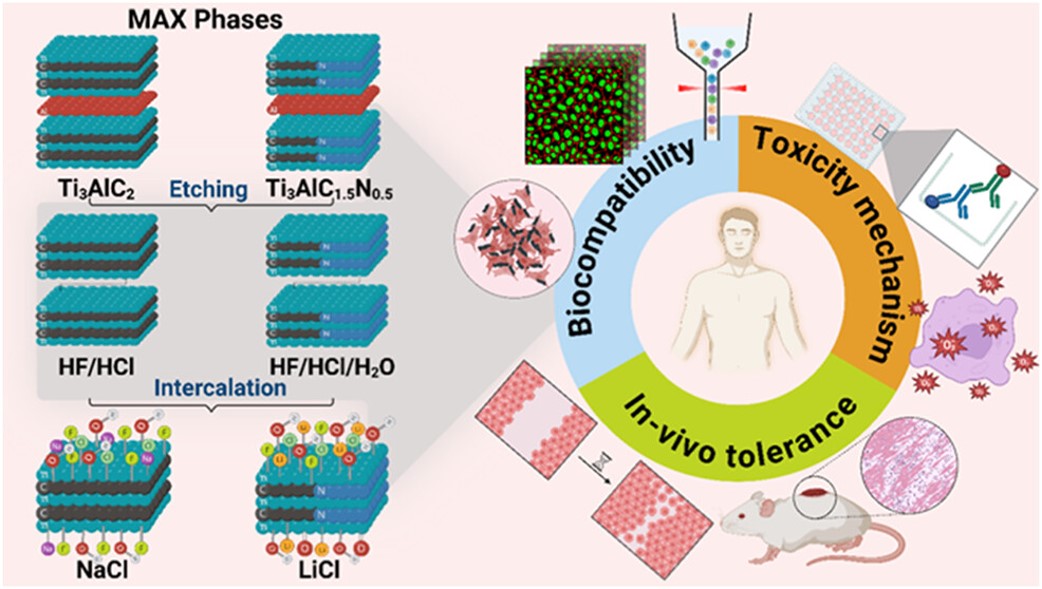 MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.
MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.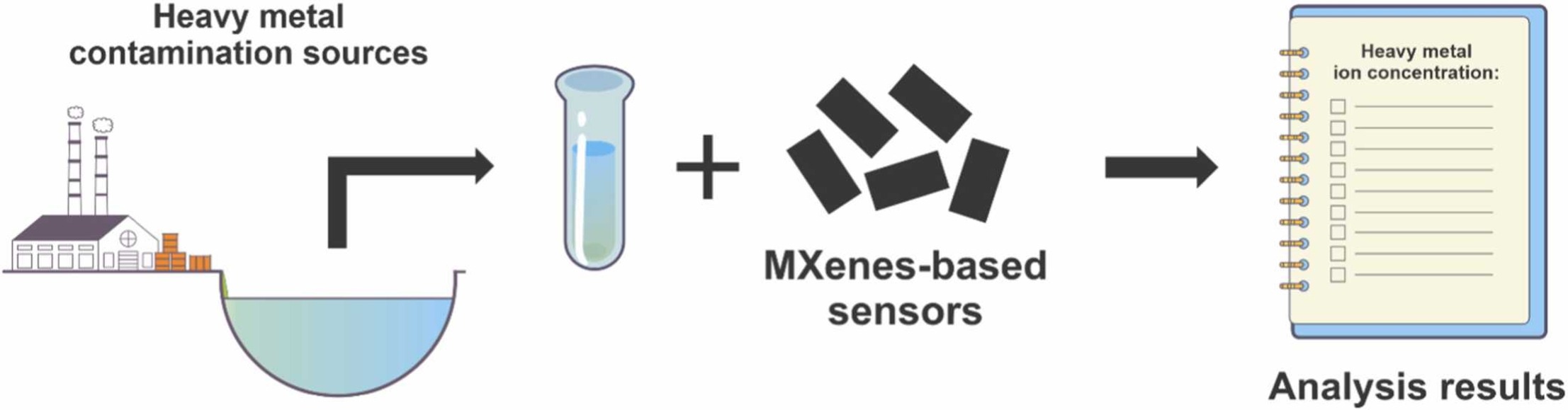 An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
 Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme.
Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme. Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved!
Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved! Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!
Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!  Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!
Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!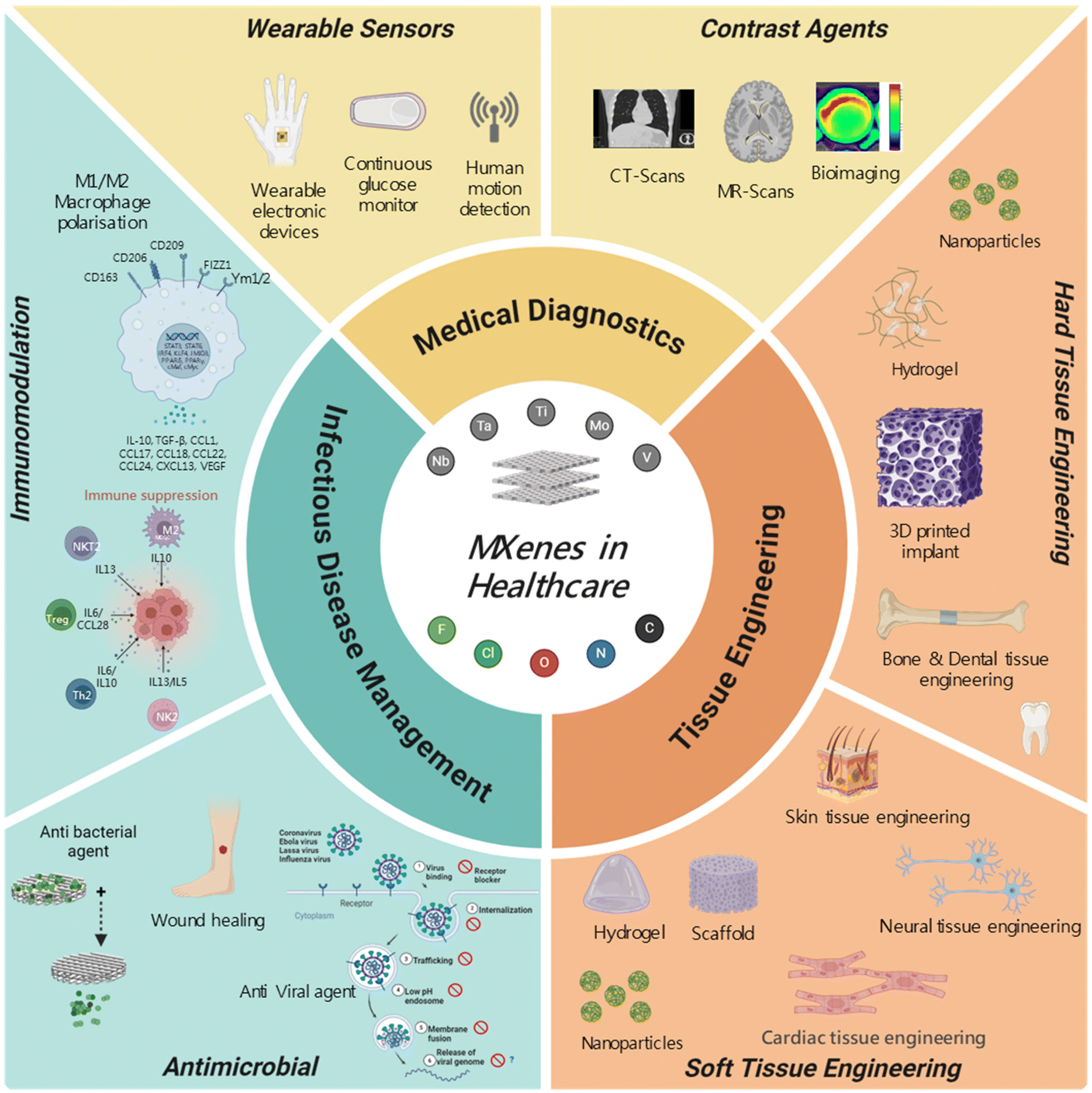 We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.
We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.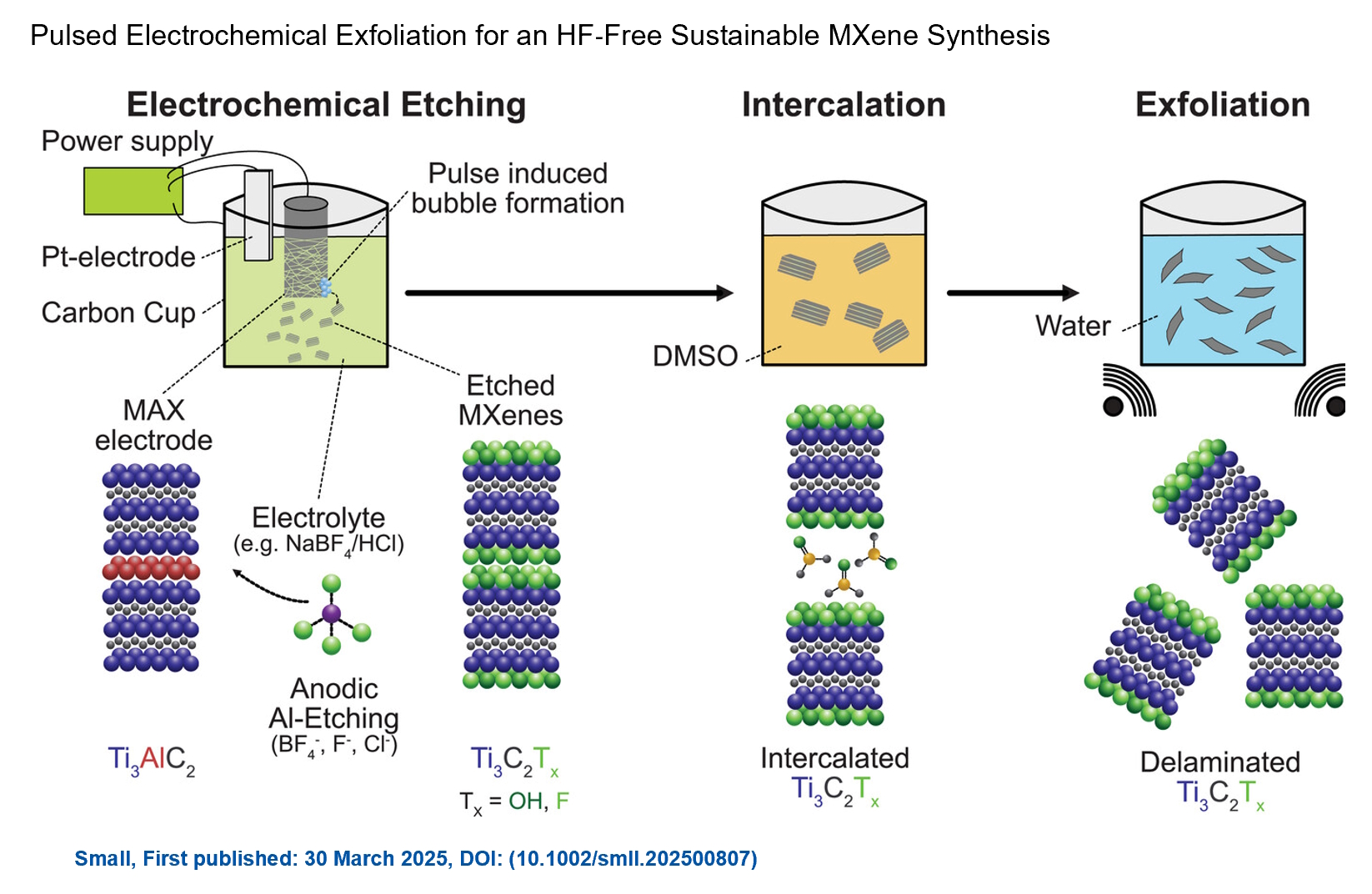 Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.
Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved. Congratulations to all collaborators with this interesting joint work!
Congratulations to all collaborators with this interesting joint work!