 |
Based on the studies involving MRC, international edition Applied Ceramic Technology has published the paper about photo-catalytic properties of tungsten oxide and titanium dioxide on brass substrate as well as practical application of the given coatings for brass products
Photocatalytic WO3 and TiO2 Films on Brass
Olha Mashtalir1,2, Murat Kurtoglu2,3,†, Sergey Pogulay1, Alexey Gogotsi1, Michael Naguib2, Yury Gogotsi2
1 Materials Research Centre, Kiev, 03680, Ukraine
2 Department of Materials Science and Engineering, A.J. Drexel Nanotechnology Institute, Drexel University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
3 Gurallar ArtCraft Inc., Kutahya, Turkey
†Department of Chemistry, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA
Cite: Mashtalir, O., Kurtoglu, M., Pogulay, S., Gogotsi, A., Naguib, M. and Gogotsi, Y. (2012), Photocatalytic WO3 and TiO2 Films on Brass. International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7402.2012.02843.x
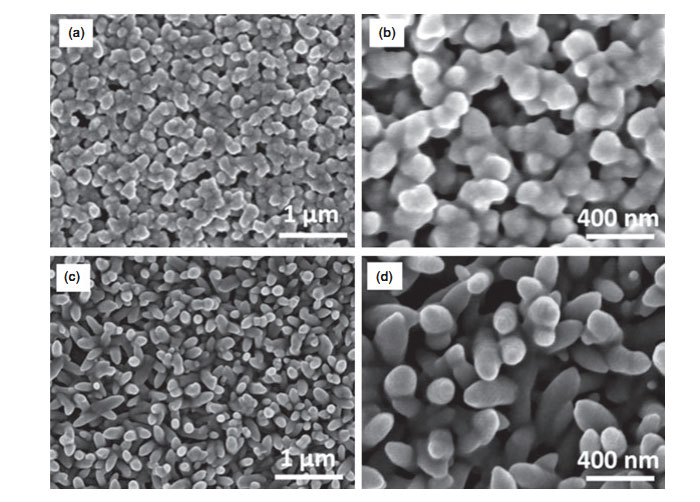
This paper reports on the structure, mechanical, and photocatalytic properties of titanium dioxide (TiO2) and tungsten oxide (WO3) films on a brass substrate. TiO2 and WO3 films have been successfully deposited on brass by a simple sol-gel dip-coating method and it has been shown that, while both films possess photocatalytic properties, WO3 films were superior to TiO2. Higher surface area and rod-like morphology of WO3 films might have contributed to their higher photocatalytic activity. Nanoindentation results have shown that both films attach well to the substrate and possess good mechanical properties.
On the SEM picture: brass with titanium dioxide coating (а, b) and brass surface covered with tungsten oxide (с, d)
Over the last few decades, interest in heterogeneous photocatalysis has been growing because of its promising applications in self-cleaning and antibacterial coatings, water and air purification systems, solar cells, and hydrogen production by water dissociation.
TiO2 has been one of the most studied materials among transition metal oxides because of its unique photoinduced catalytic activity, superhydrophilicity, nontoxicity, physical stability, and chemical inertness. Although TiO2 is still the gold standard, many other semiconductors, such as WO3, CdS, SnO2, SiO2, ZrO2, ZnO, Nb2O3,Fe2O3, SrTiO3, etc., have also been identified as potential photocatalysts. In particular, tungsten oxide (WO3) is a widely studied material because of its high photoactivity.
Therefore, film-substrate compatibility is an additional consideration required when selecting photocatalysts for film applications. While glass and ceramic materials are still the most popular of all substrates for photocatalytic films, metals have also attracted some attention, with the majority of research performed on stainless steel.
Brass is a very common decorative material because of its bright gold-like appearance and is widely used on railings, door handles, and other components that are touched by hands and would benefit from anti-bacterial coatings. Decorative panels on constructions would benefit from self-cleaning and protective coatings that would help to maintain the gold-like appearance of polished surfaces for a longer time.
That is why titanium dioxide and tungsten oxide films on a brass substrate were chosen as the subject of the study. Firstly one evaluated photocatalytic and mechanical properties of both films and then the results were compared with each other to study out what semiconductor is more promising as a photocatalitically active film on brass for practical applications.
Related items:



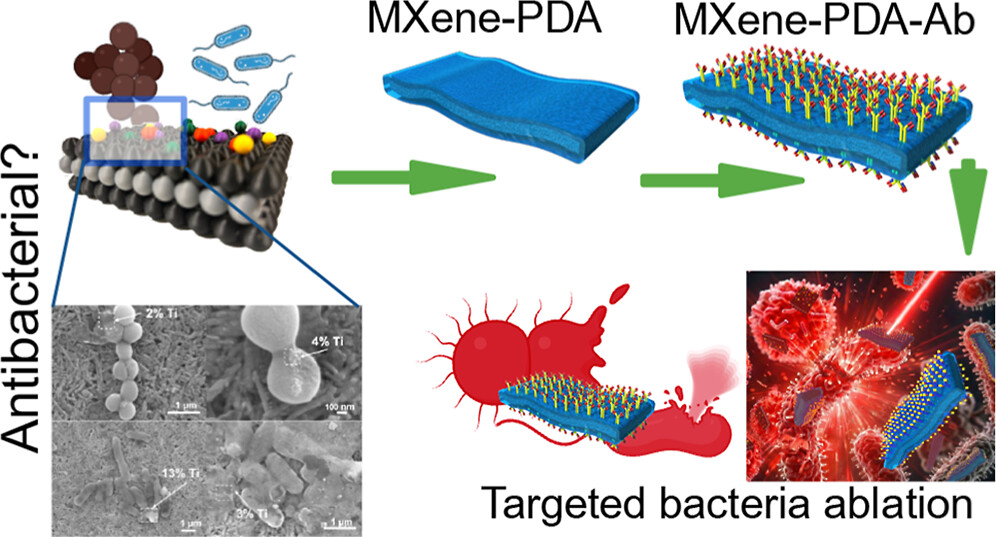 Do MXene nanosheets possess intrinsic antibacterial activity? A systematic study of high-quality Ti-, V-, and Nb-based MXenes reveals negligible inherent antimicrobial effects while highlighting their strong potential for targeted photothermal antibacterial therapy.
Do MXene nanosheets possess intrinsic antibacterial activity? A systematic study of high-quality Ti-, V-, and Nb-based MXenes reveals negligible inherent antimicrobial effects while highlighting their strong potential for targeted photothermal antibacterial therapy. Highlights
Highlights We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development.
We are excited to share that our Carbon-Ukraine (Y-Carbon LLC) company participated in the I2DM Summit and Expo 2025 at Khalifa University in Abu-Dhabi! Huge thanks to Research & Innovation Center for Graphene and 2D Materials (RIC2D) for hosting such a high-level event.It was an incredible opportunity to meet brilliant researchers and innovators working on the next generation of 2D materials. The insights and energy from the summit will definitely drive new ideas in our own development. Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments.
Carbon-Ukraine team had the unique opportunity to visit XPANCEO - a Dubai-based deep tech startup company that is developing the first smart contact lenses with AR vision and health monitoring features, working on truly cutting-edge developments. Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
Our Carbon-Ukraine team (Y-Carbon LLC) are thrilled to start a new RIC2D project MX-Innovation in collaboration with Drexel University Yury Gogotsi and Khalifa University! Amazing lab tours to project collaborators from Khalifa University, great discussions, strong networking, and a wonderful platform for future collaboration.
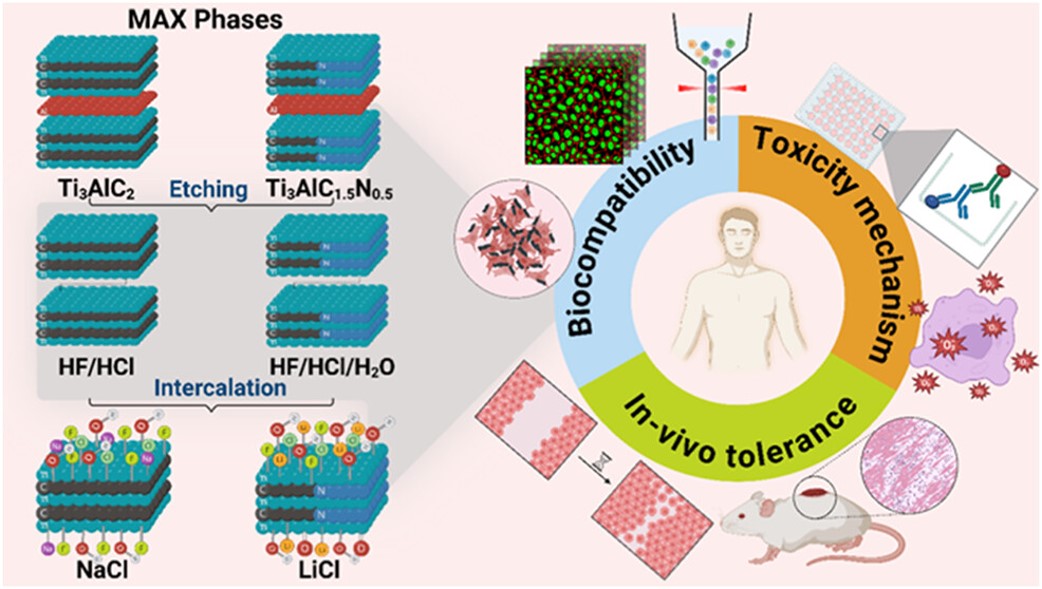 MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.
MXenes potential applications include sensors, wound healing materials, and drug delivery systems. A recent study explored how different synthesis methods affect the safety and performance of MXenes. By comparing etching conditions and intercalation strategies, researchers discovered that fine-tuning the surface chemistry of MXenes plays a crucial role in improving biocompatibility. These results provide practical guidelines for developing safer MXenes and bring the field one step closer to real biomedical applications.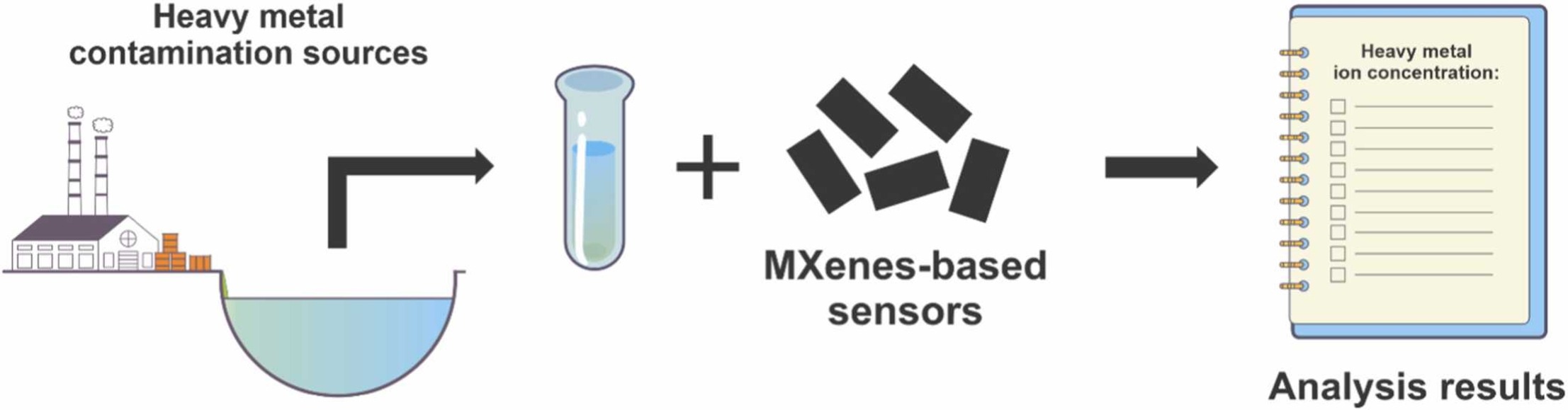 An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
An excellent review highlighting how MXene-based sensors can help tackle one of today’s pressing environmental challenges — heavy metal contamination. Excited to see such impactful work moving the field of environmental monitoring and sensor technology forward!
 Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme.
Carbon-Ukraine team was truly delighted to take part in the kickoff meeting of the ATHENA Project (Advanced Digital Engineering Methods to Design MXene-based Nanocomposites for Electro-Magnetic Interference Shielding in Space), supported by NATO through the Science for Peace and Security Programme. Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved!
Exellent news, our joint patent application with Drexel University on highly porous MAX phase precursor for MXene synthesis published. Congratulations and thanks to all team involved! Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!
Our team was very delighted to take part in International Symposium "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene event in Europe this year!  Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!
Last Call! Have you submitted your abstract for IEEE NAP-2025 yet? Join us at the International Symposium on "The MXene Frontier: Transformative Nanomaterials Shaping the Future" – the largest MXene-focused conference in Europe this year! Final Submission Deadline: May 15, 2025. Don’t miss this exclusive opportunity to showcase your research and engage with world leaders in the MXene field!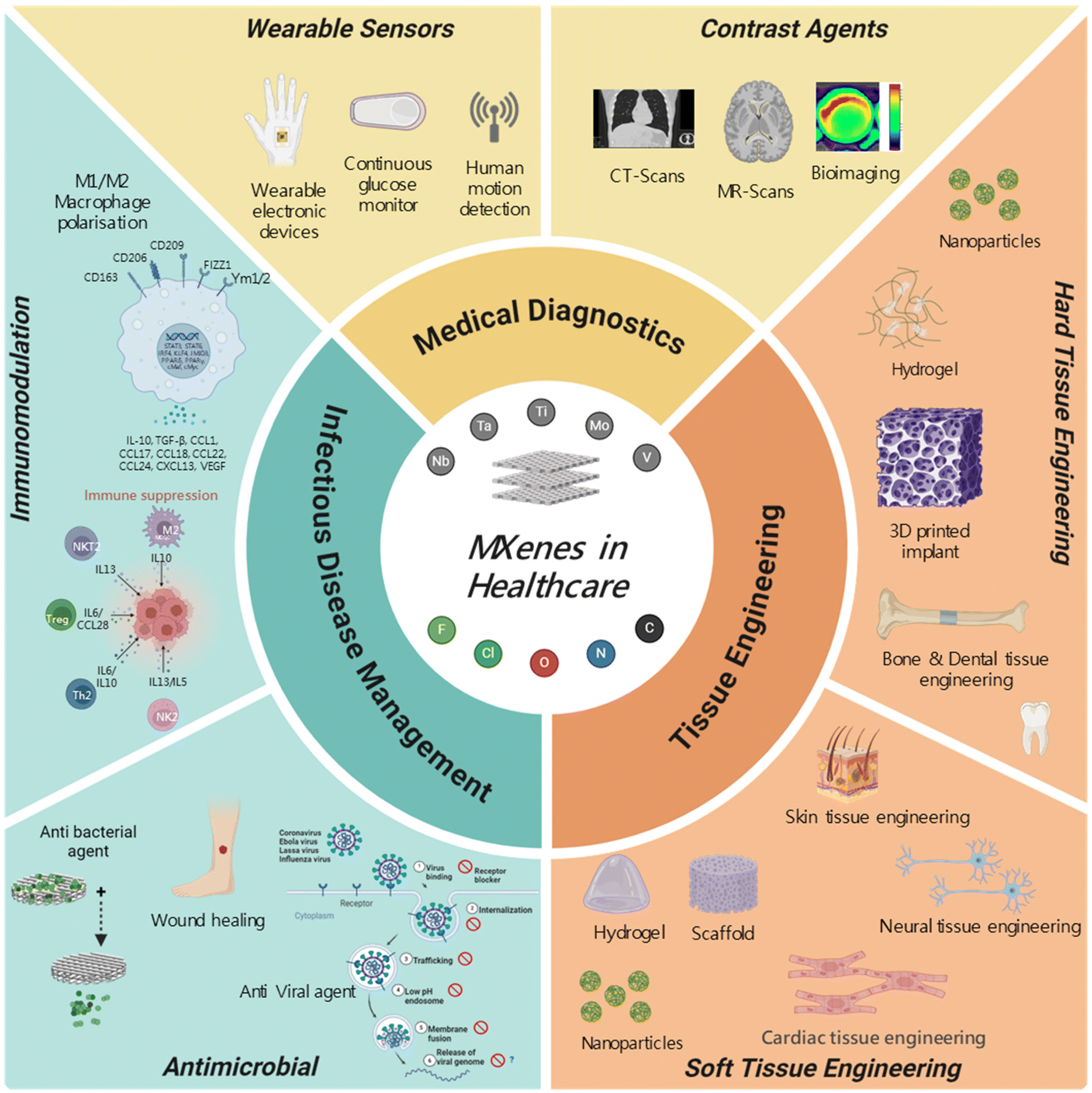 We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.
We are excited to announce the publication of latest review article on MXenes in Healthcare. This comprehensive review explores the groundbreaking role of MXenes—an emerging class of 2D materials—in revolutionizing the fields of medical diagnostics and therapeutics. Read the full article here: https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR04853A.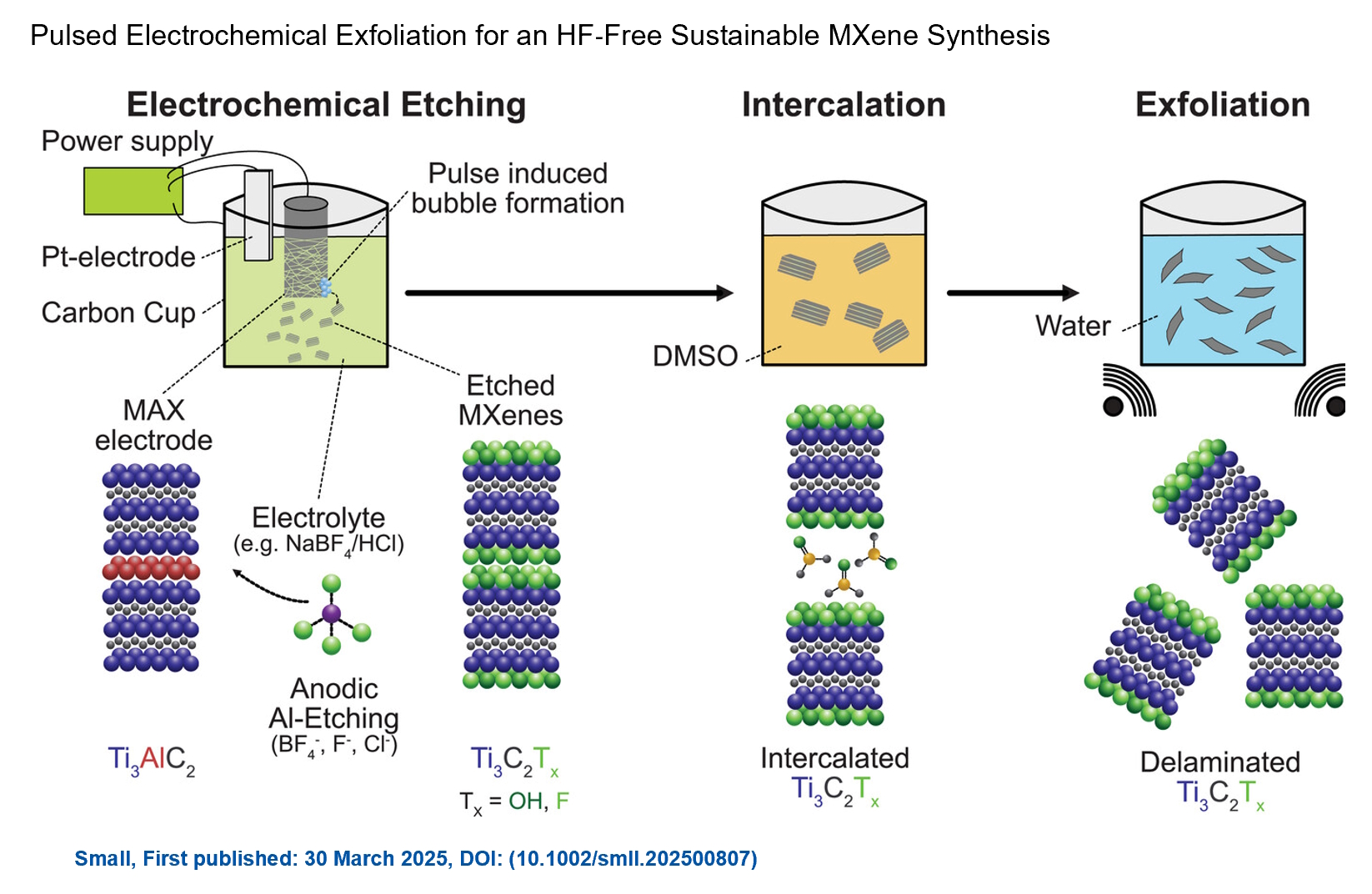 Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.
Congratulations and thank you to our collaborators from TU Wien and CEST for very interesting work and making it published! In this work, an upscalable electrochemical MXene synthesis is presented. Yields of up to 60% electrochemical MXene (EC-MXene) with no byproducts from a single exfoliation cycle are achieved.